Introduction to SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify and analyze an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The acronym SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This framework is essential for businesses, nonprofit organizations, and even individuals to make informed decisions and establish effective strategies.
History and Development
The SWOT framework was developed by Albert Humphrey in the 1960s and 1970s at the Stanford Research Institute. Initially created for business applications based on data from Fortune 500 companies, it has since been adopted by various organizations for strategic planning and decision-making.
Purpose and Benefits
The primary goal of SWOT analysis is to increase awareness of the factors that influence business decisions or strategies. It helps organizations uncover opportunities for success and identify threats before they become significant issues. SWOT analysis can also assist in identifying market niches where a business has a competitive advantage and guide individuals in plotting career paths that maximize their strengths.
When and Why to Conduct a SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is typically used at the beginning of or as part of a strategic planning process. It is a powerful tool for decision-making as it enables organizations to uncover previously unarticulated opportunities for success and highlights threats before they become overly burdensome.
Effective Use of SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is most effective when it pragmatically recognizes and includes business issues and concerns. It often involves a diverse cross-functional team capable of sharing thoughts and ideas freely. Using actual experiences and data, such as revenue or cost figures, can enhance the effectiveness of the analysis.
Elements of a SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis examines four key elements:
- Strengths: Internal attributes and resources that support a successful outcome, such as a diverse product line, loyal customers, or strong customer service.
- Weaknesses: Internal factors and resources that make success more difficult to attain, such as a weak brand, excessive debt, or inadequate staffing or training.
- Opportunities: External factors that the organization can capitalize on or take advantage of, such as favorable export tariffs, tax incentives, or new enabling technologies.
- Threats: External factors that could jeopardize the entity’s success, such as increasing competition, weakening demand, or an uncertain supply chain.
SWOT Matrix
A SWOT matrix is often used to organize the items identified under each of these four elements. The matrix is usually a square divided into four quadrants, with each quadrant representing one of the specific elements. Decision-makers identify and list specific strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in their respective quadrants.
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Conducting a SWOT analysis involves the following steps:
- Specify the Objective: Clearly define the goal or objective you hope to achieve for the business, organization, initiative, or individual.
- Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: List the internal strengths and weaknesses of the entity.
- Identify Opportunities and Threats: List the external opportunities and threats that could impact the entity.
- Use Guiding Questions: Tools and questions can guide the decision-making process. For example, to identify strengths, ask questions like “What do you do better than anyone else?” and “What advantages do you have?”
Example of a SWOT Analysis
The following is an example of a SWOT analysis for an imaginary retail employee:
- Strengths: Good communication skills, punctuality, handles customers well, gets along with all departments, physical strength, good availability.
- Weaknesses: Takes long smoke breaks, has low technical skill, prone to spending time chatting.
- Opportunities: Storefront worker, greeting customers, assisting them to find products, keeping customers satisfied, assisting customers post-purchase, stocking shelves.
- Threats: Occasionally missing time during peak business due to breaks, spending too much time per customer post-sale, too much time in interdepartmental chat.
Using a SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps an entity gain insight into its current and future position in the marketplace or against a stated goal. It allows organizations to see competitive advantages, positive prospects, and existing and potential problems. With this information, they can develop business plans or personal or organizational goals to capitalize on positives and address deficiencies.
Applications of SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis can be used to assess and consider a range of goals and action plans, such as:
- The creation and development of business products or services.
- Making hiring, promotion, or other human resources decisions.
- Evaluating and improving customer service opportunities and performance.
- Setting business strategies to improve competitiveness or business performance.
- Making investments in technologies, geographical locations, or markets.
Comparison with PEST Analysis
SWOT analysis is similar to PEST analysis, which stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological. PEST analysis helps organizations analyze external factors that affect their operations and competitiveness.
Pros and Cons of SWOT Analysis
Advantages
- Creates a visual representation of the factors impacting success.
- Encourages diverse perspectives and approaches.
- Fleshes out each element and exposes creative ideas and overlooked problems.
Limitations
- May not include all relevant factors.
- Input can be empirical or subjective, giving a skewed perspective.
- Captures factors at a particular point in time, limiting its shelf life.
Case Study: SWOT Analysis of Nike
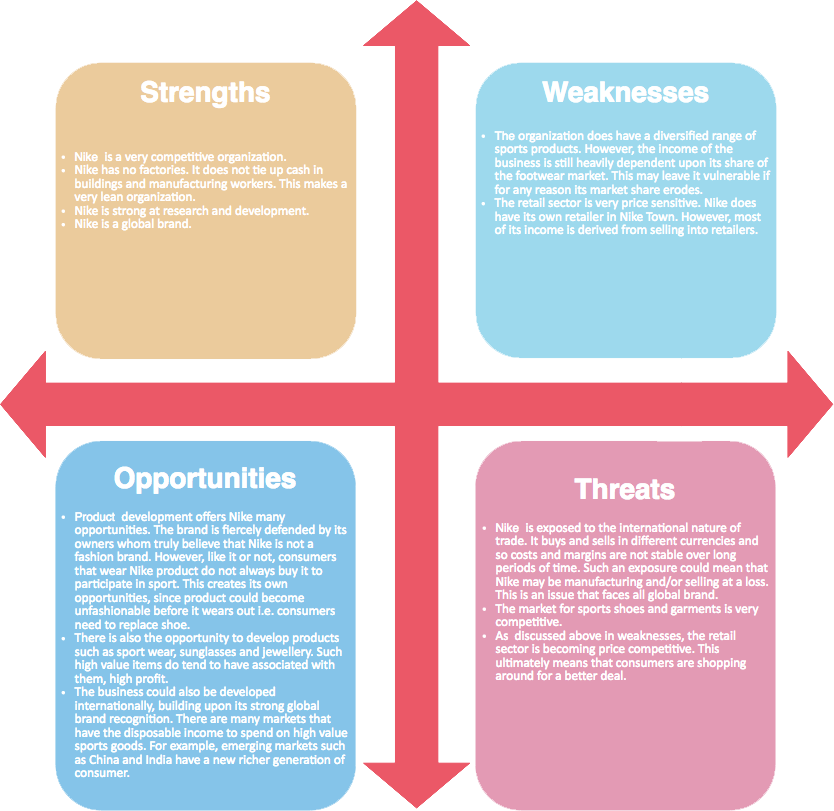
Strengths
- Highly competitive organization.
- Lean organization with no factories, reducing cash tied up in buildings and manufacturing workers.
- Strong research and development capabilities.
- Global brand recognition.
Weaknesses
- Diversified range of sports products but heavily dependent on the footwear market.
- Price-sensitive retail sector.
- Limited own retailer presence, with most income derived from selling into retailers.
Opportunities
- Product development offers many opportunities.
- Strong brand loyalty and association with sports.
- Potential to develop products in clothing and jewelry.
- International expansion, particularly in markets with disposable income like China and India.
Threats
- Exposure to international trade risks, including currency fluctuations and economic downturns.
- Highly competitive market for sports shoes and garments.
- Price competition in the retail sector.
Analysis
Nike’s SWOT analysis highlights its strengths in research and development, global brand recognition, and a lean organizational structure. However, it also faces weaknesses such as dependence on the footwear market and a price-sensitive retail sector. Opportunities for Nike include product development, brand loyalty, and international expansion. Threats include exposure to international trade risks and a highly competitive market.
By conducting a SWOT analysis, Nike can develop strategies to capitalize on its strengths and opportunities while addressing its weaknesses and threats. This analysis provides a comprehensive view of Nike’s position in the market and guides its strategic planning and decision-making processes.
Conclusion
SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for strategic planning and decision-making. By identifying and analyzing an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, it helps uncover opportunities for success and highlights potential threats. Whether used by businesses, nonprofit organizations, or individuals, SWOT analysis provides a structured approach to understanding the internal and external factors that impact success.
References
- SWOT Analysis Tutorial: This tutorial explains what SWOT analysis is, how to perform it, and provides a step-by-step guide to improve your business. It includes examples and discusses the importance of understanding the business environment for achieving goals. Read more
- SWOT Analysis Tutorial – Visual Paradigm Online: This resource guides organizations in identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a product. It includes examples and discusses the strategic decision-making process. Read more
- Free UML, BPMN and Agile Tutorials – Learn Step-by-Step: This page offers a variety of tutorials, including a SWOT analysis tutorial. It provides step-by-step instructions on specific topics and regularly adds new tutorials. Read more
- Comprehensive Tutorial for SWOT Analysis – Visual Paradigm: A detailed guide on conducting a SWOT analysis, including steps to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Read more
- SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide – Visual Paradigm: An in-depth guide explaining what SWOT analysis is, why it’s used, and how to conduct one, with examples. Read more
- Quick Guide to SWOT Analysis – Cybermedian: A concise guide explaining the SWOT analysis method, internal vs external factors, and steps to conduct the analysis. Read more
- How to Use SWOT Analysis – Cybermedian: A guide on understanding and using SWOT analysis, including examples and templates. Read more
- How to Do SWOT Analysis – Cybermedian: A detailed article on performing a SWOT analysis, covering internal and external factors, and developing an action plan. Read more

