Introduction
Tech Innovate Solutions is a leading technology company specializing in software development, IT consulting, and digital transformation services. As the company grew, it recognized the need for a structured approach to enterprise architecture to align its IT strategy with business goals, improve operational efficiency, and enhance agility.
This case study explores how Tech Innovate Solutions applied the TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework to establish and operate an effective Enterprise Architecture practice.
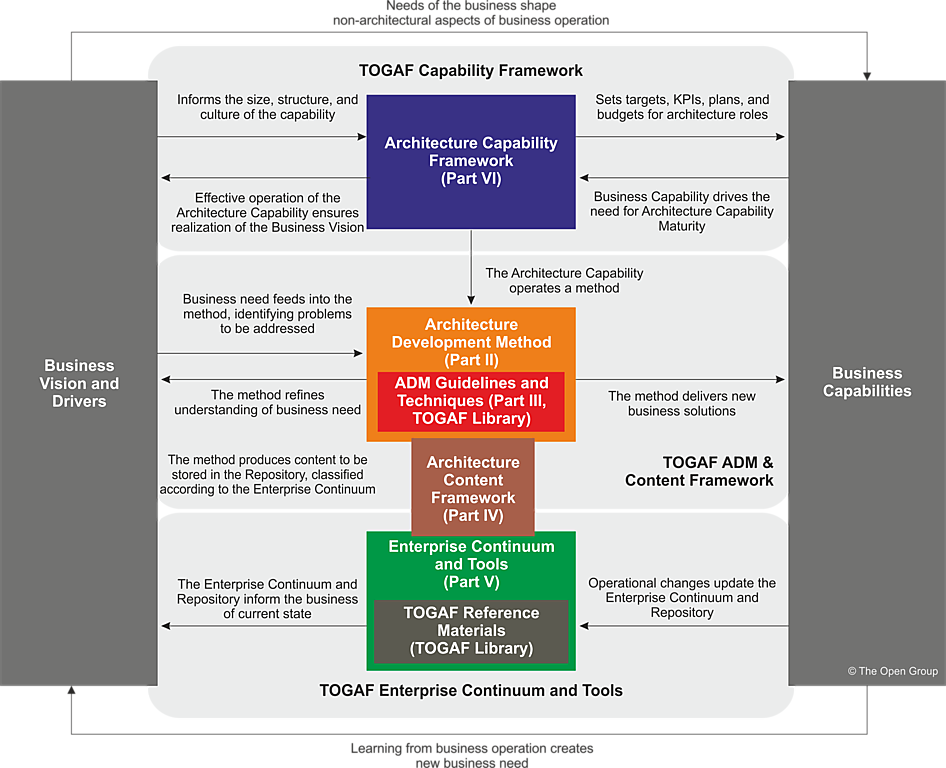
Background
Tech Innovate Solutions had been experiencing challenges in aligning its IT initiatives with business objectives. The lack of a structured enterprise architecture framework resulted in siloed decision-making, inefficient resource allocation, and misaligned IT projects. The company decided to adopt the TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework to address these issues and establish a robust enterprise architecture practice.
Establishing the Architecture Capability
Reviewing the Organizational Context
The first step was to review the organizational context for conducting Enterprise Architecture. Tech Innovate Solutions identified the following key drivers:
- Business Drivers: Improve operational efficiency, enhance agility, and align IT strategy with business goals.
- Stakeholders: Senior management, IT department, business units, and external consultants.
- Requirements: Develop a structured enterprise architecture framework, improve IT governance, and enhance collaboration between business and IT.
Identifying Stakeholders, Concerns, and Requirements
Tech Innovate Solutions engaged with key stakeholders to understand their concerns and requirements. The following were identified:
- Senior Management: Concerned with aligning IT strategy with business goals and improving operational efficiency.
- IT Department: Needed a structured approach to architecture development and governance.
- Business Units: Required better collaboration with the IT department and more efficient IT services.
Defining the Scope of the Architecture Work
The scope of the architecture work was defined to include the following areas:
- Business Units: Sales, Marketing, Finance, and Operations.
- IT Systems: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and digital platforms.
- Processes: IT governance, architecture development, and compliance.
Tailoring the TOGAF Framework
Tech Innovate Solutions tailored the TOGAF framework to meet its specific needs. This included:
- Customizing the ADM: Adapting the Architecture Development Method (ADM) to fit the company’s processes and workflows.
- Content Framework: Developing a content framework to structure architecture descriptions and work products.
- Content Metamodel: Defining a content metamodel to describe the components and inter-relationships of the architecture.
Defining the Architecture Principles
The following architecture principles were defined to guide the architecture development process:
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensure that IT initiatives align with business objectives.
- Agility: Promote agility and flexibility in IT systems and processes.
- Collaboration: Enhance collaboration between business and IT.
- Governance: Implement robust IT governance and compliance processes.
Establishing the Enterprise Architecture Team and Organization
Tech Innovate Solutions established an Enterprise Architecture team with the following roles and responsibilities:
- Enterprise Architect: Responsible for overseeing the architecture development process and ensuring alignment with business goals.
- Business Architect: Focused on aligning IT strategy with business objectives and improving operational efficiency.
- Solution Architect: Responsible for designing and implementing IT solutions that meet business requirements.
- IT Architect: Focused on the technical aspects of architecture development and governance.
Developing Strategy and Implementation Plans for Tools and Techniques
A strategy and implementation plan for the tools and techniques required to support enterprise architecture activities was developed. This included:
- Architecture Development Tools: Tools for architecture modeling, documentation, and governance.
- Collaboration Platforms: Platforms for enhancing collaboration between business and IT.
- Governance and Compliance Tools: Tools for monitoring and enforcing architecture compliance and governance.
Implementing Architecture Governance
Establishing the Architecture Board
Tech Innovate Solutions established an Architecture Board to oversee the architecture development process. The board was responsible for:
- Reviewing and Approving Architecture Deliverables: Ensuring that architecture deliverables align with business goals and architecture principles.
- Ensuring Compliance with Architecture Principles: Monitoring and enforcing compliance with the established architecture principles.
- Making Decisions Related to Architecture Governance: Defining architecture standards, policies, and procedures.
Implementing Processes for Architecture Compliance
Processes for architecture compliance were implemented, including:
- Compliance Criteria: Defining criteria for assessing compliance with architecture principles and standards.
- Compliance Review Processes: Establishing processes for reviewing and approving architecture compliance.
- Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement: Implementing mechanisms for monitoring and enforcing architecture compliance.
Monitoring and Enforcing Architecture Governance
Mechanisms for monitoring and enforcing architecture governance were implemented, including:
- Governance Metrics: Defining metrics for assessing the effectiveness of architecture governance.
- Governance Reviews: Conducting regular governance reviews to assess compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Corrective Actions: Taking corrective action when necessary to address governance issues.
Enhancing Architecture Maturity
Assessing Current Capabilities
Tech Innovate Solutions assessed its current capabilities in Enterprise Architecture, identifying the following areas for improvement:
- Processes: The need for more structured and efficient architecture development processes.
- Roles and Responsibilities: The need for clearer definitions of roles and responsibilities within the Enterprise Architecture team.
- Skills and Competencies: The need for enhanced skills and competencies in enterprise architecture.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
The following areas for improvement were identified:
- Process Improvement: The need for more efficient and effective architecture development processes.
- Role Clarity: The need for clearer definitions of roles and responsibilities within the Enterprise Architecture team.
- Skills Development: The need for enhanced skills and competencies in enterprise architecture.
Developing a Maturity Improvement Plan
A maturity improvement plan was developed to address the identified areas for improvement. This included:
- Process Improvement Initiatives: Initiatives to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of architecture development processes.
- Role and Responsibility Clarification: Initiatives to clarify the roles and responsibilities within the Enterprise Architecture team.
- Skills Development Programs: Programs to enhance the skills and competencies of the Enterprise Architecture team.
Developing the Architecture Skills Framework
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of the Enterprise Architecture team were defined as follows:
- Enterprise Architect: Responsible for overseeing the architecture development process and ensuring alignment with business goals.
- Business Architect: Focused on aligning IT strategy with business objectives and improving operational efficiency.
- Solution Architect: Responsible for designing and implementing IT solutions that meet business requirements.
- IT Architect: Focused on the technical aspects of architecture development and governance.
Identifying Required Skills and Competencies
The following skills and competencies were identified as required for effective enterprise architecture practice:
- Architecture Development: Knowledge of architecture development methods and tools.
- IT Governance: Knowledge of IT governance principles and practices.
- Business Acumen: Understanding of business objectives and the ability to align IT strategy with business goals.
- Collaboration: The ability to collaborate effectively with business and IT stakeholders.
Developing a Skills Improvement Plan
A skills improvement plan was developed to enhance the skills and competencies of the Enterprise Architecture team. This included:
- Training Programs: Programs to develop the knowledge and skills required for effective enterprise architecture practice.
- Mentoring and Coaching: Initiatives to provide mentoring and coaching to the Enterprise Architecture team.
- Certification: Initiatives to obtain certification in enterprise architecture and related disciplines.
Summary of Findings
Introduction: TechInnovate Solutions, a leading technology company, adopted the TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework to address challenges in aligning IT initiatives with business objectives, improve operational efficiency, and enhance agility.
Background:
- Challenges: Siloed decision-making, inefficient resource allocation, and misaligned IT projects.
- Objective: Establish a robust enterprise architecture practice using the TOGAF framework.
Establishing the Architecture Capability:
- Reviewing the Organizational Context:
- Business Drivers: Improve operational efficiency, enhance agility, and align IT strategy with business goals.
- Stakeholders: Senior management, IT department, business units, and external consultants.
- Requirements: Develop a structured enterprise architecture framework, improve IT governance, and enhance collaboration between business and IT.
- Identifying Stakeholders, Concerns, and Requirements:
- Senior Management: Concerned with aligning IT strategy with business goals and improving operational efficiency.
- IT Department: Needed a structured approach to architecture development and governance.
- Business Units: Required better collaboration with the IT department and more efficient IT services.
- Defining the Scope of the Architecture Work:
- Areas Covered: Sales, Marketing, Finance, Operations, ERP, CRM, and digital platforms.
- Processes: IT governance, architecture development, and compliance.
- Tailoring the TOGAF Framework:
- Customizing the ADM: Adapting the Architecture Development Method (ADM) to fit the company’s processes and workflows.
- Content Framework: Developing a content framework to structure architecture descriptions and work products.
- Content Metamodel: Defining a content metamodel to describe the components and inter-relationships of the architecture.
- Defining the Architecture Principles:
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensure that IT initiatives align with business objectives.
- Agility: Promote agility and flexibility in IT systems and processes.
- Collaboration: Enhance collaboration between business and IT.
- Governance: Implement robust IT governance and compliance processes.
- Establishing the Enterprise Architecture Team and Organization:
- Roles: Enterprise Architect, Business Architect, Solution Architect, IT Architect.
- Responsibilities: Overseeing architecture development, aligning IT strategy with business objectives, designing IT solutions, and focusing on technical aspects of architecture development and governance.
- Developing Strategy and Implementation Plans for Tools and Techniques:
- Tools: Architecture modeling, documentation, governance, collaboration platforms, and governance and compliance tools.
Implementing Architecture Governance:
- Establishing the Architecture Board:
- Responsibilities: Reviewing and approving architecture deliverables, ensuring compliance with architecture principles, and making decisions related to architecture governance.
- Implementing Processes for Architecture Compliance:
- Compliance Criteria: Defining criteria for assessing compliance with architecture principles and standards.
- Compliance Review Processes: Establishing processes for reviewing and approving architecture compliance.
- Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement: Implementing mechanisms for monitoring and enforcing architecture compliance.
- Monitoring and Enforcing Architecture Governance:
- Governance Metrics: Defining metrics for assessing the effectiveness of architecture governance.
- Governance Reviews: Conducting regular governance reviews to assess compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Corrective Actions: Taking corrective action when necessary to address governance issues.
Enhancing Architecture Maturity:
- Assessing Current Capabilities:
- Areas for Improvement: Processes, roles and responsibilities, skills and competencies.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement:
- Process Improvement: Need for more efficient and effective architecture development processes.
- Role Clarity: Need for clearer definitions of roles and responsibilities within the Enterprise Architecture team.
- Skills Development: Need for enhanced skills and competencies in enterprise architecture.
- Developing a Maturity Improvement Plan:
- Initiatives: Process improvement, role and responsibility clarification, skills development programs.
Developing the Architecture Skills Framework:
- Defining Roles and Responsibilities:
- Enterprise Architect: Overseeing architecture development and ensuring alignment with business goals.
- Business Architect: Aligning IT strategy with business objectives and improving operational efficiency.
- Solution Architect: Designing and implementing IT solutions that meet business requirements.
- IT Architect: Focusing on the technical aspects of architecture development and governance.
- Identifying Required Skills and Competencies:
- Architecture Development: Knowledge of architecture development methods and tools.
- IT Governance: Knowledge of IT governance principles and practices.
- Business Acumen: Understanding of business objectives and the ability to align IT strategy with business goals.
- Collaboration: Ability to collaborate effectively with business and IT stakeholders.
- Developing a Skills Improvement Plan:
- Training Programs: Developing knowledge and skills for effective enterprise architecture practice.
- Mentoring and Coaching: Providing mentoring and coaching to the Enterprise Architecture team.
- Certification: Obtaining certification in enterprise architecture and related disciplines.
Conclusion
By applying the TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework, Tech Innovate Solutions was able to establish and operate an effective Enterprise Architecture practice. The framework provided a structured approach to developing the necessary capabilities, processes, roles, and governance mechanisms to support enterprise architecture activities. This resulted in improved alignment between IT strategy and business goals, enhanced operational efficiency, and better collaboration between business and IT. The TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework proved to be a valuable tool for establishing a robust enterprise architecture practice at Tech Innovate Solutions.
By applying the TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework, TechInnovate Solutions established a structured and effective Enterprise Architecture practice. This resulted in improved alignment between IT strategy and business goals, enhanced operational efficiency, and better collaboration between business and IT. The framework provided a comprehensive approach to developing the necessary capabilities, processes, roles, and governance mechanisms to support enterprise architecture activities.
Reference List for ArchiMate and TOGAF
- TOGAF® Tool for Enterprise Architecture – ArchiMetric
- Description: This resource provides an overview of TOGAF ADM and how Visual Paradigm supports the development of TOGAF deliverables using ArchiMate diagrams.
- URL: TOGAF® Tool for Enterprise Architecture
- Navigating the Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate 2.1 to 3.2 – ArchiMetric
- Description: This guide discusses the evolution of ArchiMate, its alignment with TOGAF, and the advanced features of Visual Paradigm for ArchiMate modeling.
- URL: Navigating the Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate 2.1 to 3.2
- Mastering Enterprise Architecture with Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF Tool – ArchiMetric
- Description: This article highlights the features of Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF tool, including support for ArchiMate and TOGAF ADM, and its benefits for enterprise architecture.
- URL: Mastering Enterprise Architecture with Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF Tool
- What is ArchiMate? – Visual Paradigm
- Description: A step-by-step learning guide on ArchiMate, its integration with TOGAF, and how it complements existing methods like UML and BPMN.
- URL: What is ArchiMate?
- Using BPMN to Supplement TOGAF ADM EA Development Together with ArchiMate – ArchiMetric
- Description: This resource discusses the integration of BPMN with TOGAF ADM and ArchiMate, and the comprehensive modeling support provided by Visual Paradigm.
- URL: Using BPMN to Supplement TOGAF ADM EA Development Together with ArchiMate
- Understanding Abstraction in the ArchiMate Language – ArchiMetric
- Description: This article explains the abstraction concepts in ArchiMate and how Visual Paradigm supports effective modeling and design.
- URL: Understanding Abstraction in the ArchiMate Language
- An Overview of ArchiMate – the Enterprise Architecture Modeling Language – Cybermedian
- Description: This overview discusses ArchiMate’s integration with TOGAF and other frameworks, and the benefits of using Visual Paradigm for ArchiMate modeling.
- URL: An Overview of ArchiMate
- Deal with Enterprise Complexity with Visual Paradigm Just-in-Time Process – ArchiMetric
- Description: This resource discusses Visual Paradigm’s Just-in-Time process composer and its integration with TOGAF ADM and ArchiMate for managing enterprise complexity.
- URL: Deal with Enterprise Complexity with Visual Paradigm Just-in-Time Process
- Visual Paradigm TOGAF – Everything about TOGAF, Enterprise Architecture, ArchiMate, and more
- Description: This guide provides an in-depth look at ArchiMate 3, TOGAF, and enterprise architecture, and how Visual Paradigm supports these frameworks.
- URL: Visual Paradigm TOGAF
- Free Online ArchiMate Tool + Examples – Cybermedian
- Description: This resource offers free online ArchiMate tools and examples, highlighting the integration of ArchiMate with TOGAF and the support provided by Visual Paradigm.
- URL: Free Online ArchiMate Tool + Examples
These references provide a comprehensive overview of ArchiMate and TOGAF, their integration, and the tools available on Visual Paradigm to support enterprise architecture modeling.

