Introduction
In today’s complex business environment, ensuring that different systems and parts of an organization can effectively share information and services is crucial. This is where interoperability comes into play. Additionally, managing the relationships between various management frameworks is essential for the successful implementation of enterprise architecture. This guide will delve into the concepts of interoperability and the relationships between management frameworks, with a focus on the TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) standard.
Understanding Interoperability
Definition and Importance
Interoperability is defined as the ability to share information and services. It is a critical architectural requirement, especially in complex organizations, as it ensures that different parts of the enterprise can work together seamlessly. The determination of interoperability is present throughout the Architecture Development Method (ADM) in the TOGAF framework.
Phases of Interoperability in ADM
- Technology Architecture Phase (Phase D):
- In this phase, appropriate technical mechanisms for information and service exchanges are specified. This ensures that the technical infrastructure supports the required level of interoperability.
- Opportunities & Solutions Phase (Phase E):
- Actual solutions, such as Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) packages, are selected. This phase focuses on identifying the best solutions that meet the interoperability requirements.
- Migration Planning Phase (Phase F):
- Interoperability is logically implemented in this phase. This involves planning the transition to the new architecture while ensuring that interoperability is maintained throughout the migration process.
Categories of Interoperability
- Operational or Business Interoperability:
- Defines how different parts of the enterprise work together at the business level or how business processes are shared. This ensures that business operations are aligned and can function cohesively.
- Information Interoperability:
- Defines how information is to be shared. This category focuses on ensuring that data and information can be exchanged seamlessly between different systems and applications.
- Technical Interoperability:
- Defines how technical resources are to be shared or connected. This involves ensuring that the technical infrastructure supports the required level of interoperability.
IT Perspective on Interoperability
From an IT perspective, interoperability can also be considered in terms of Enterprise Application Integration (EAI):
- Presentation Integration/Interoperability:
- A common look-and-feel through a common portal-like solution guides the user to the underlying functionality of systems. This ensures a consistent user experience across different applications.
- Information Integration/Interoperability:
- Corporate information is seamlessly shared between various corporate applications, often based on a common corporate ontology and shared services. This ensures that data is consistent and accessible across the enterprise.
- Application Integration/Interoperability:
- Corporate functionality is integrated and shareable so that applications are not duplicated and are seamlessly linked through functionality such as workflow. This is closely linked to corporate business process unification/interoperability.
- Technical Integration/Interoperability:
- Common methods and shared services for communication, storage, processing, and access to data in application platforms and communication infrastructures. This ensures that the technical infrastructure supports the required level of interoperability.
Refining Interoperability Requirements
Interoperability requirements should be refined to meet the needs of the enterprise and/or extended enterprise in an unambiguous way. Clear measures of interoperability are key to success and should be part of the Enterprise Architecture’s strategic direction. Interoperability is a key consideration in system of systems or federated models. The degree of rationalization of the corporate IT infrastructure, based on standards and/or common IT platforms, impacts interoperability.
Relationships Between Management Frameworks
Overview
The TOGAF framework is designed to co-exist with and enhance the operational capabilities of other management frameworks within an organization. The main frameworks that should be coordinated with the TOGAF framework include:
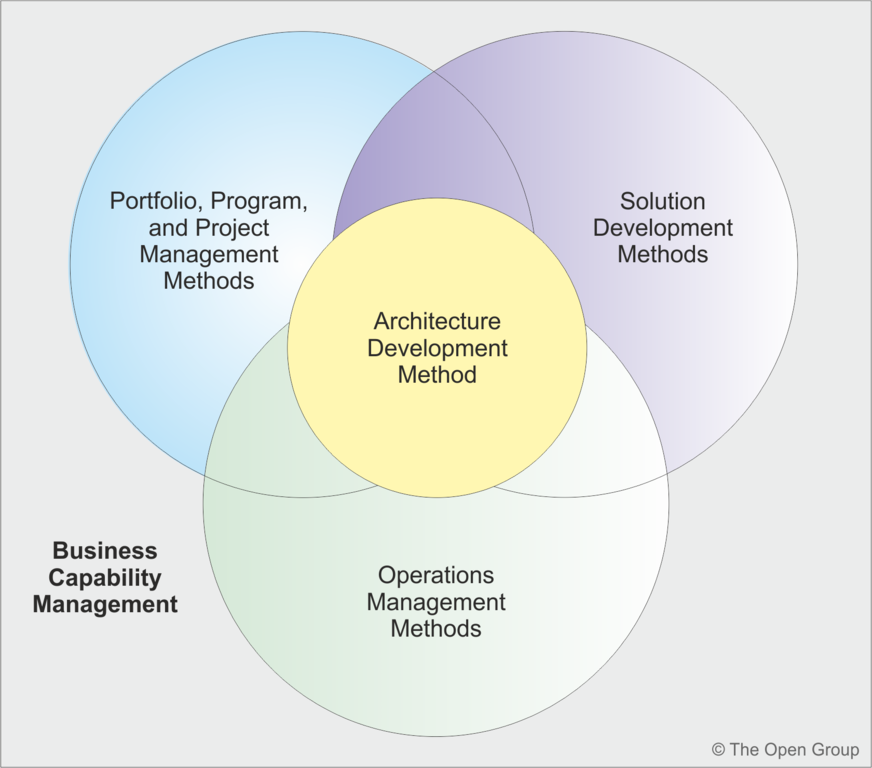
- Business Capability Management:
- Determines what business capabilities are required to deliver business value, including return on investment and performance measures.
- Project/Portfolio Management Methods:
- Determine how a company manages its change initiatives.
- Operations Management Methods:
- Describe how a company runs its day-to-day operations, including IT.
- Solution Development Methods:
- Formalize how business systems are delivered in accordance with IT architecture structures.
Integration of Frameworks
These frameworks are not discrete and have significant overlaps, particularly with Business Capability Management. Enterprise Architects must be aware of the impact of architecture on the entire enterprise and not narrowly focus on IT implementation.
- The Enterprise Architecture:
- Provides a structure for all corporate initiatives. It serves as the blueprint for how the enterprise should be organized and how different components should interact.
- Portfolio Management Framework:
- Used to deliver the components of the architecture. This framework ensures that the right projects are selected and executed to support the enterprise architecture.
- Operations Management Framework:
- Supports incorporating new components within the corporate infrastructure. This framework ensures that new systems and processes are integrated seamlessly into the existing infrastructure.
Coordination and Harmony
The management frameworks must complement each other and work in harmony for the good of the enterprise. The TOGAF approach delivers a framework for Enterprise Architecture. Project/portfolio management is the delivery framework that receives structured direction for planning and building deliverables that fit into the corporate architecture. Operations management receives deliverables and integrates/sustains them within the corporate infrastructure.
Implementation and Migration Plan
The Implementation and Migration Plan needs to be coordinated with the management frameworks within the organization, including Business Capability Management, Project/Portfolio Management, Operations Management, and Solution Development Methods. Existing models from various sources, when integrated, may not necessarily result in a coherent Enterprise Architecture. The Architecture Governance Framework is integral to the Enterprise Continuum and manages content relevant to both the architectures themselves and to architecture governance processes.
Conclusion
In summary, interoperability is crucial for ensuring that different systems and parts of an organization can effectively share information and services. The TOGAF framework is designed to work alongside other management frameworks, with each framework contributing to different aspects of the enterprise. Coordinating these frameworks is essential for the successful implementation of enterprise architecture. The relationships between the frameworks involve the Enterprise Architecture providing structure, Portfolio Management delivering components, and Operations Management supporting the integration of new components. By understanding and managing these relationships, organizations can achieve a coherent and effective enterprise architecture.
Reference List for ArchiMate and TOGAF
- TOGAF® Tool for Enterprise Architecture – ArchiMetric
- Description: This resource provides an overview of TOGAF ADM and how Visual Paradigm supports the development of TOGAF deliverables using ArchiMate diagrams.
- URL: TOGAF® Tool for Enterprise Architecture
- Navigating the Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate 2.1 to 3.2 – ArchiMetric
- Description: This guide discusses the evolution of ArchiMate, its alignment with TOGAF, and the advanced features of Visual Paradigm for ArchiMate modeling.
- URL: Navigating the Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide to ArchiMate 2.1 to 3.2
- Mastering Enterprise Architecture with Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF Tool – ArchiMetric
- Description: This article highlights the features of Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF tool, including support for ArchiMate and TOGAF ADM, and its benefits for enterprise architecture.
- URL: Mastering Enterprise Architecture with Visual Paradigm’s TOGAF Tool
- What is ArchiMate? – Visual Paradigm
- Description: A step-by-step learning guide on ArchiMate, its integration with TOGAF, and how it complements existing methods like UML and BPMN.
- URL: What is ArchiMate?
- Using BPMN to Supplement TOGAF ADM EA Development Together with ArchiMate – ArchiMetric
- Description: This resource discusses the integration of BPMN with TOGAF ADM and ArchiMate, and the comprehensive modeling support provided by Visual Paradigm.
- URL: Using BPMN to Supplement TOGAF ADM EA Development Together with ArchiMate
- Understanding Abstraction in the ArchiMate Language – ArchiMetric
- Description: This article explains the abstraction concepts in ArchiMate and how Visual Paradigm supports effective modeling and design.
- URL: Understanding Abstraction in the ArchiMate Language
- An Overview of ArchiMate – the Enterprise Architecture Modeling Language – Cybermedian
- Description: This overview discusses ArchiMate’s integration with TOGAF and other frameworks, and the benefits of using Visual Paradigm for ArchiMate modeling.
- URL: An Overview of ArchiMate
- Deal with Enterprise Complexity with Visual Paradigm Just-in-Time Process – ArchiMetric
- Description: This resource discusses Visual Paradigm’s Just-in-Time process composer and its integration with TOGAF ADM and ArchiMate for managing enterprise complexity.
- URL: Deal with Enterprise Complexity with Visual Paradigm Just-in-Time Process
- Visual Paradigm TOGAF – Everything about TOGAF, Enterprise Architecture, ArchiMate, and more
- Description: This guide provides an in-depth look at ArchiMate 3, TOGAF, and enterprise architecture, and how Visual Paradigm supports these frameworks.
- URL: Visual Paradigm TOGAF
- Free Online ArchiMate Tool + Examples – Cybermedian
- Description: This resource offers free online ArchiMate tools and examples, highlighting the integration of ArchiMate with TOGAF and the support provided by Visual Paradigm.
- URL: Free Online ArchiMate Tool + Examples
These references provide a comprehensive overview of ArchiMate and TOGAF, their integration, and the tools available on Visual Paradigm to support enterprise architecture modeling.
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













