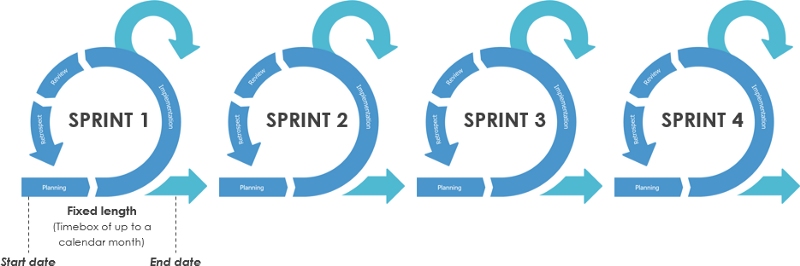
Agile development is a human-centric, iterative, and gradual development method. In agile development, the construction of a software project is divided into multiple sub-projects, and the results of each sub-project have been tested and have the characteristics of integration and operation.
In other words, a large project is divided into multiple small projects that are interrelated but can also be run independently, and completed separately. During this process, the software is always in a usable state.
Classification of agile development models
Agile is a mindset and it’s a set of values and principles. Agile is a way of thinking and acting. Agile is all about short cycles, iterative and incremental delivery, failing fast, getting feedback, delivering business value to customers early and about people, collaboration and interaction. Agile is a mindset which is all about transparency, inspection and adaptation. Agile however doesn’t consist of any roles, events or artifacts. It’s a mindset. For example, Scrum is one of the widely used frameworks under the Agile umbrella, which may help you in becoming more Agile, there are however many more frameworks within the Agile movement, like Kanban, XP, Crystal and many more as shown in the Figure below:
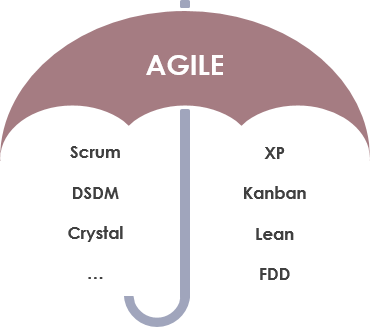
- XP Extreme Programming (eXtreme Programming)
- SCRUM
- Kanban
- Lean
- Crystal method
- Dynamic system development method
Among them, XP and SCRUM are the most popular.
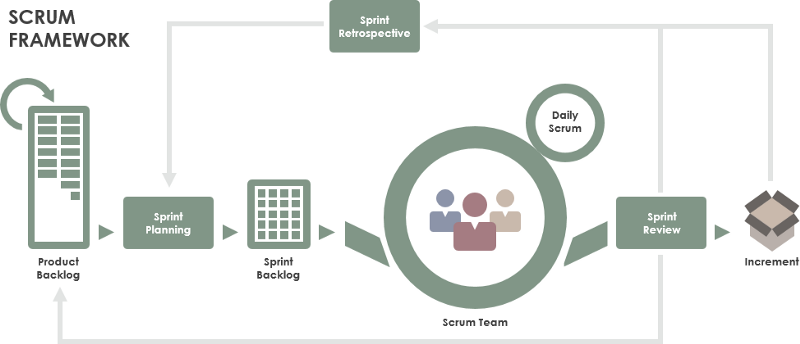
Scrum
Scrum is a framework within which people can address complex adaptive problems, while productively and creatively delivering products of the highest possible value. It is used for managing software projects and product or application development. Its focus is on an adaptive product development strategy where a cross-functional team works as a unit to reach a common goal within 2–4 weeks (Sprint). It consists of a collection of values, artifacts, roles, ceremonies, rules and best practices.
Lean
Lean originated with the Toyota Production System, or TPS, which revolutionized the manufacture of physical goods in the 1950s, ’60s, and beyond. Lean maintains its hold in manufacturing but has also found new applications in knowledge work, helping businesses in all industries eliminate waste, improve processes, and boost innovation. Software development is a natural application of Lean methodology because, much like manufacturing, it generally follows a defined process, has some defined conditions of acceptance, and results in the delivery of tangible value. The key concepts that guide all practice of Lean methodology, which we call the Pillars of Lean. They are:
- Continuous improvement
- Respect for people
- Lightweight Leadership
Kanban
Kanban is a highly visual workflow management method that is popular among Lean teams. In fact, 83% of teams practicing Lean use Kanban to visualize and actively manage the creation of products with an emphasis on continual delivery, while not overburdening the development team. Like Scrum, Kanban is a process designed to help teams work together more effectively.

Kanban is based on 3 basic principles:
- Visualize what you’ll do today (workflow): Seeing all the items within the context of each other can be very informative
- Limit the amount of work in progress (WIP): This helps balance the flow-based approach so teams don‘t start and commit to too much work at once
- Enhance flow: When something is finished, the next highest priority item from the backlog is pulled into play
Kanban promotes continuous collaboration and encourages active, ongoing learning and improvement by defining the best possible team workflow.
Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
DSDM is a framework that is made up of eight principles, a lifecycle and products, roles and responsibilities and several best practice techniques. These underpin and support a philosophy of delivering strategically aligned business benefits as early as possible to give an organization the best possible return on investment (ROI).
DSDM is a methodology that prioritizes schedule and quality over functionality, which fixes cost, quality and time at the start and uses the MoSCoW method of prioritization, which breaks a project down into four different types of requirements:
- Must have (M)
- Should have (S)
- Could have ©
- Won’t have (W)
There are eight principles underpinning DSDM Atern. These principles direct the team in the attitude they must take and the mindset they must adopt to deliver consistently.
- Focus on the business need
- Deliver on time
- Collaborate
- Never compromise quality
- Build incrementally from firm foundations
- Develop iteratively
- Communicate continuously and clearly
- Demonstrate control
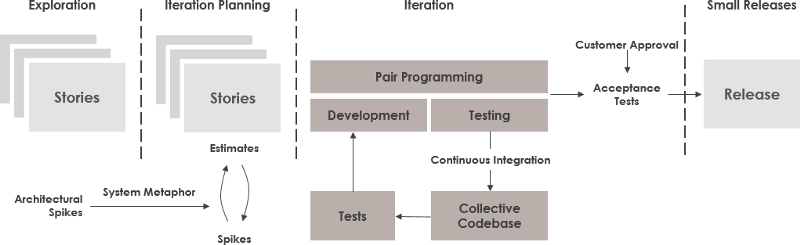
Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming (XP), originally described by Kent Beck, has emerged as one of the most popular and controversial Agile methodologies. XP is a disciplined approach to delivering high-quality software quickly and continuously. It is intended to improve software quality and responsiveness in the face of changing customer requirements. It promotes high customer involvement, rapid feedback loops, continuous testing, continuous planning, and close teamwork to deliver working software at very frequent intervals, typically every 1–3 weeks.
What are the key values of agile methods?
The term “Agile” was coined in 2001 in the Agile Manifesto. The manifesto set out to establish principles to guide a better approach to software development. The Agile Manifesto consists of 4 important values. The way to read the Agile Manifesto is not that the items on the right side have no value anymore, but the Agile movement values the items on the left more.
There are four key values that are the building blocks of each component in an Agile approach. They emphasize a shift in emphasis from practices and processes to people and collaboration.
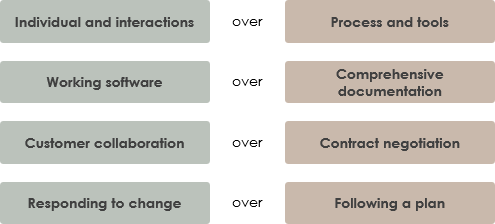
These four values inform agile best practices, focusing on flexibility so that teams can best work together to accomplish tasks. Agile practices elevate the importance of the end goal throughout the process. If people can work well together, adapt to new changes, and produce, it doesn’t matter so much how they do it.
12 best practices
Complementing the Agile Manifesto, the Agile Alliance has also defined a set of 12 underlying principles, which provide guidance and more detailed explanation in addition to the Agile Manifesto:

- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Agile processes promote sustainable development.
- The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
- Simplicity–the art of maximizing the amount of work not done–is essential.
- The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams. At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Summary
Agile Development is one of the big buzzwords of the software development industry which is a different way of managing software development projects. Rather than a specific software development method, it is an umbrella term for a set of methods and practices based on the values and principles expressed in the Agile Manifesto. Solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organizing, cross-functional teams utilizing the appropriate practices for their context.
Agile Development Reading
- What are the 8 Wastes in Lean?
- Extreme Programming (XP) vs Scrum
- What is Timeboxing in Scrum?
- Agile Myth: Documentation and Planning not Needed?
- How Scrum or LeSS Apply Empirical Process Control Principle?
- Scrum Checklist for Every Scrum Teams
- Agile Development: Sprint Zero or Not Sprint Zero?
- Top 6 Common Misconceptions in Agile Development
- Agile Framework Tools — From Small Teams to Scaling Agile
- Comparison of Agile Teams
- Why Agile Project Management? Transitioning from Traditional PM to Agile
- The Top 7 Popular Agile Development Approaches
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













