Harvard University professor Michael O ‘Neal put forward the theory of the five forces of industrial structure. He believes that there are five forces promoting industrial competition. With this structure, you can develop survival and growth strategies for your business, assess the attractiveness and expansion potential of other industries, and investigate the profitability level of an industry.
What is 5 Forces Analysis?
A Five Forces analysis can help companies assess industry attractiveness, how trends will affect industry competition, which industries a company should compete in — and how companies can position themselves for success.
Five Forces Analysis is a strategic tool designed to give a global overview, rather than a detailed business analysis technique. It helps review the strengths of a market position, based on five key forces. Thus, Five Forces works best when looking at an entire market sector, rather than your own business and a few competitors.
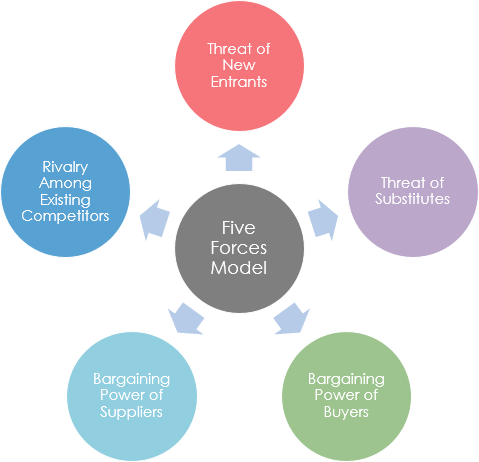
The main idea of this model is that the key to an enterprise obtaining a competitive advantage lies in the profitability (industry attraction) of the industry in which the enterprise is located and the relative competitive position of the enterprise in the industry.
Therefore, the primary task of strategic management is to select potentially highly profitable industries by analyzing five factors including suppliers, buyers, current competitors, alternative products, and potential entrants. After selecting industries, enterprises should choose one of three strategies, such as low-cost, production dissimilation or centralization, as their competitive strategy, based on their strength and the comparison of the five forces.
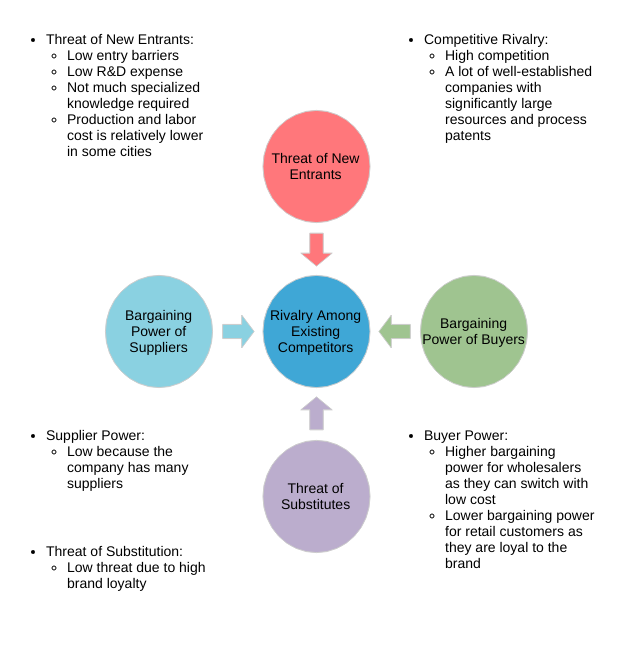
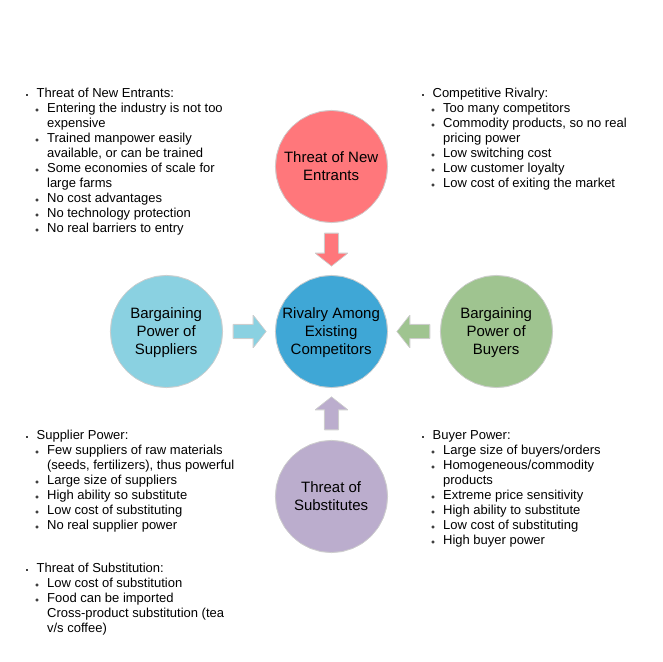
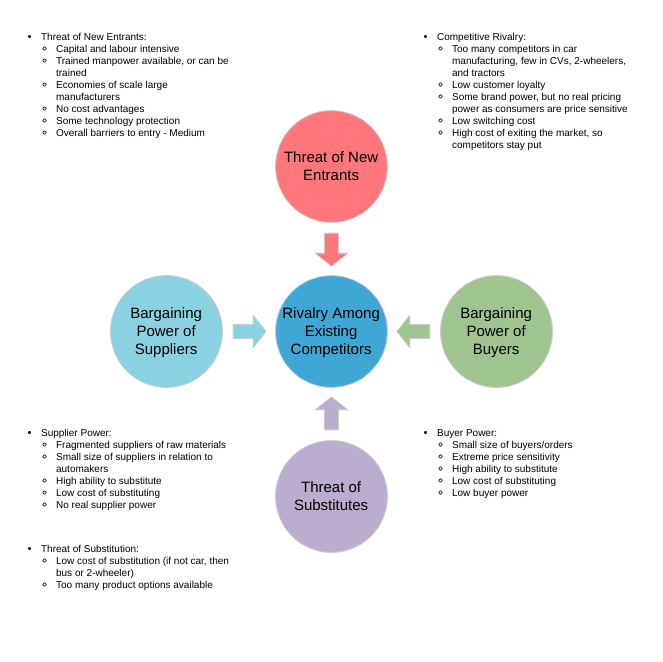
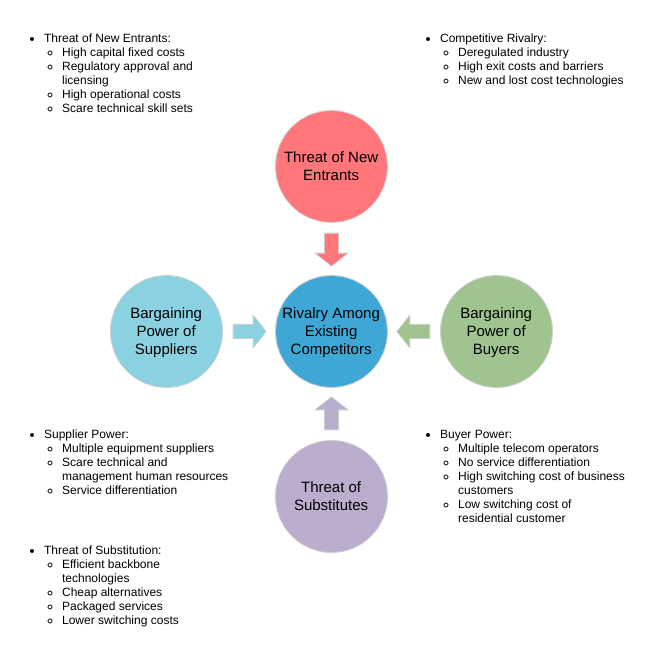
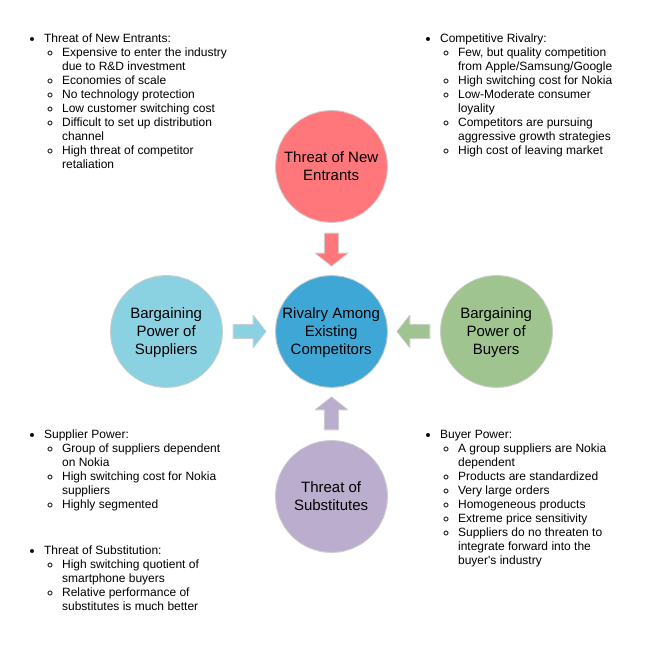
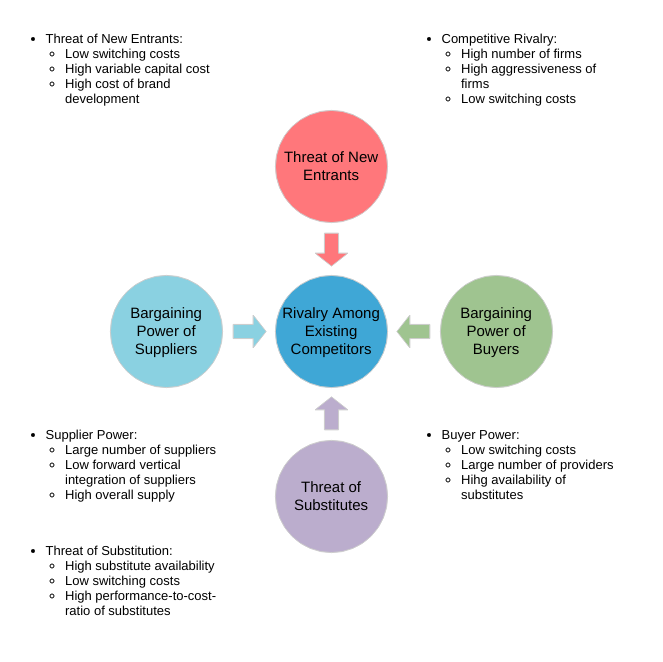
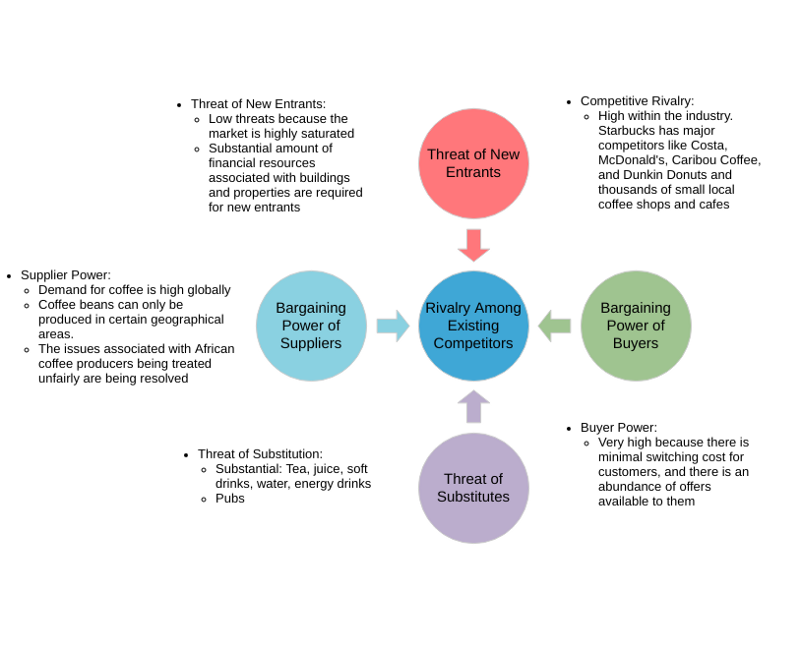
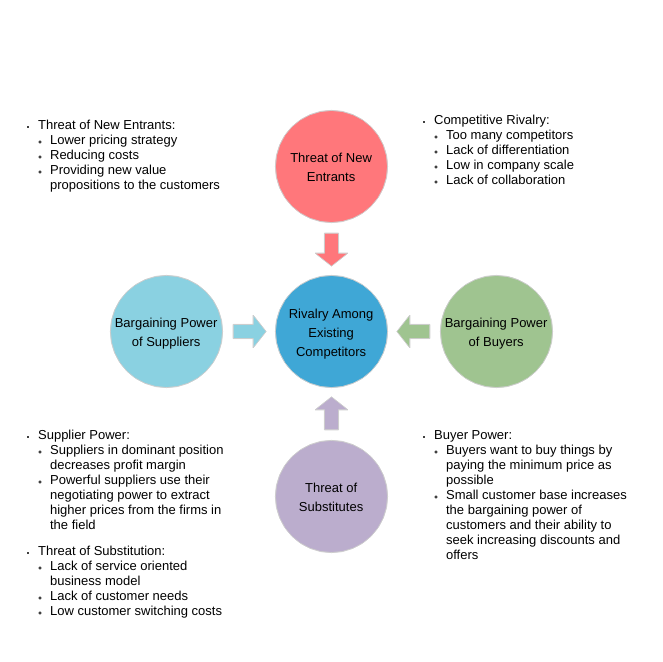
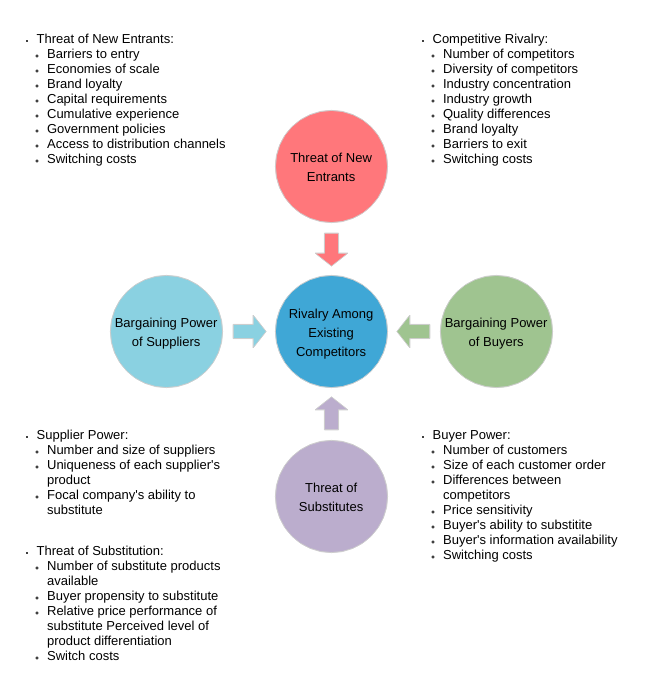
The five forces model that can be used to analyze an industry is:
- Competitor ─The degree of competition among existing manufacturers.
- Suppliers — the collective bargaining power of suppliers.
- Substitutes — the threat of substitute products or services.
- Buyer — The buyer’s overall bargaining power.
- New entrants — threats caused by new vendors that may join your market.
The assembly of these five forces will determine the profitability of the industry. Based on this, conduct a systematic analysis of the industry you want to enter:
- According to the product scale and geographic coverage, clearly understand the industry you want to enter. Before trying to analyze, think carefully about how to define an industry.
- First identify the participants who constitute these 5 forces, and classify them clearly.
- Then evaluate the fundamental driving force of each force, and judge whether the ripeness is strong or weak.
- Then sit down and think about it calmly, evaluate the entire industrial structure, and find out the most important forces in fact.
- After completing the above actions, then analyze the recent and possible future changes of each force, and try to predict how these changes will ferment in the industry.
- The last step is to try to find a market position, which is the weakest place of all kinds of forces ─ ─ That place is in your advantage position in the industrial structure.
The industry is changing from time to time. The more you understand an industry, the more likely it is to find new strategic opportunities and use it to gain an advantage sooner. Once you have a deep understanding of an industry, you can also understand the profit and loss balance of major manufacturers in the industry.
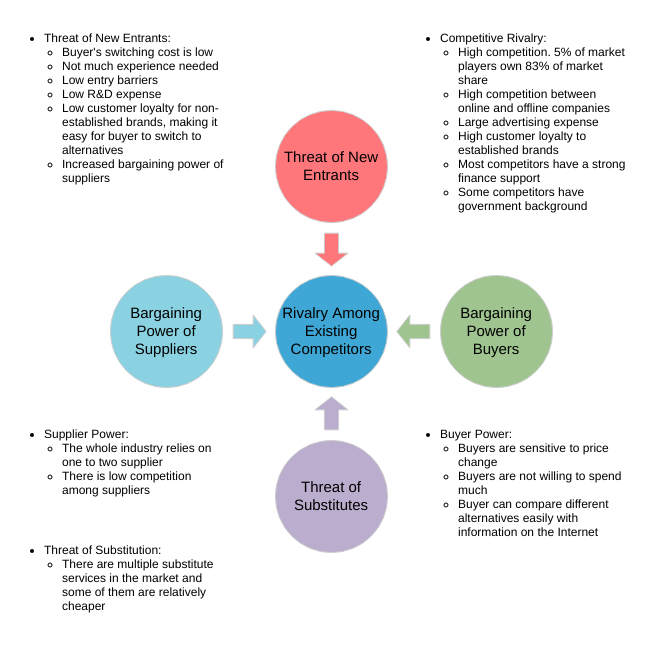
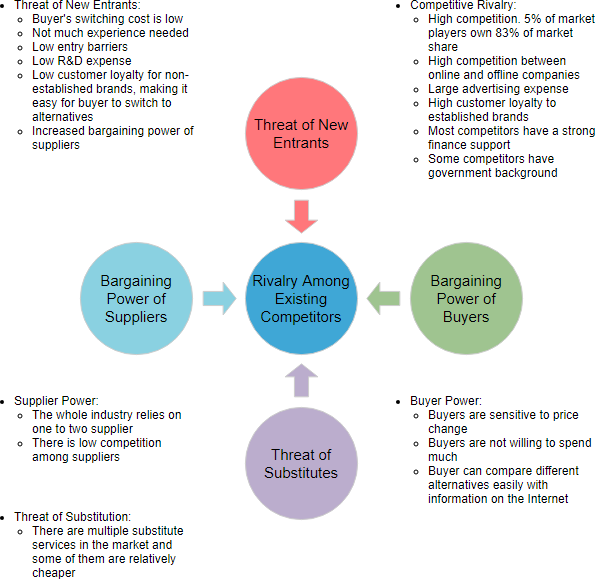
Five Forces Analysis Live Example
The Five Forces are the Threat of new market players, the threat of substitute products, power of customers, power of suppliers, industry rivalry which determines the competitive intensity and attractiveness of a market.
Explore more Five Forces Analysis templates