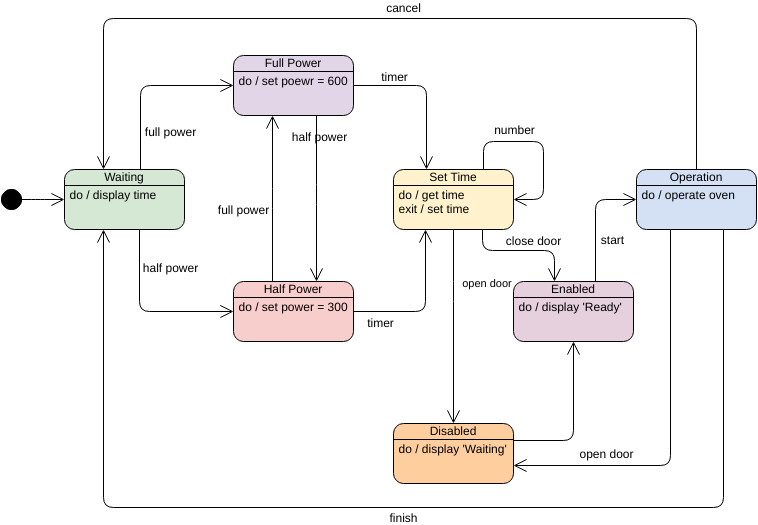
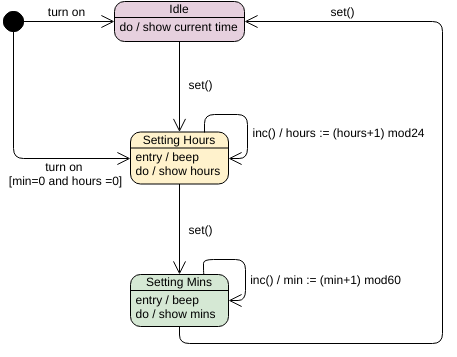
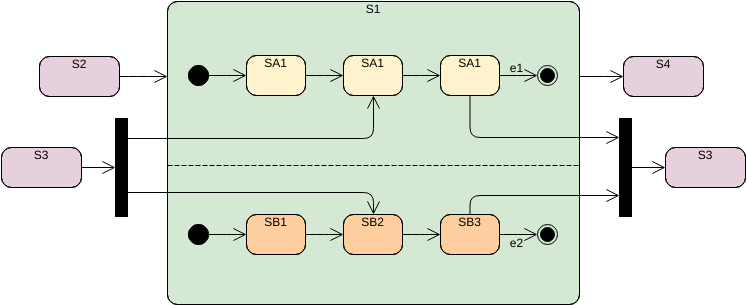
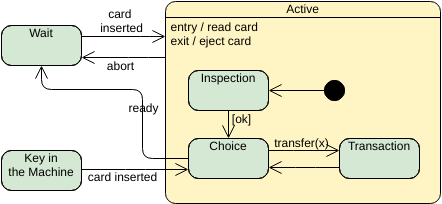
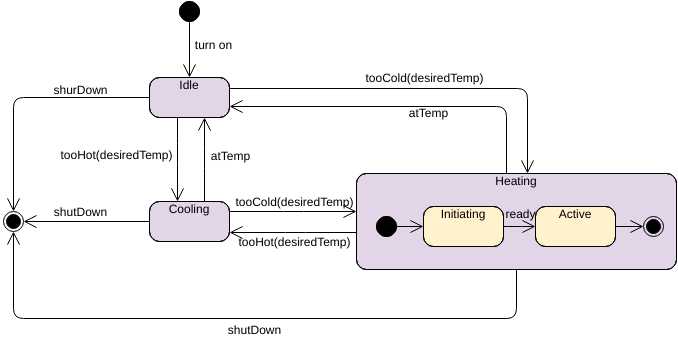
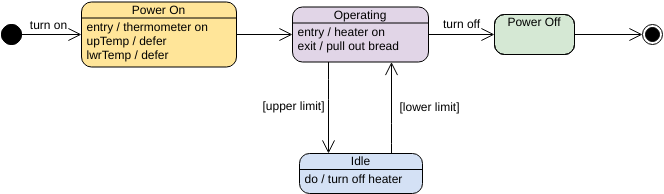
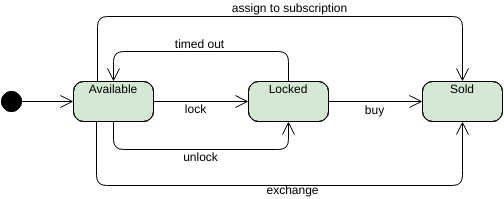
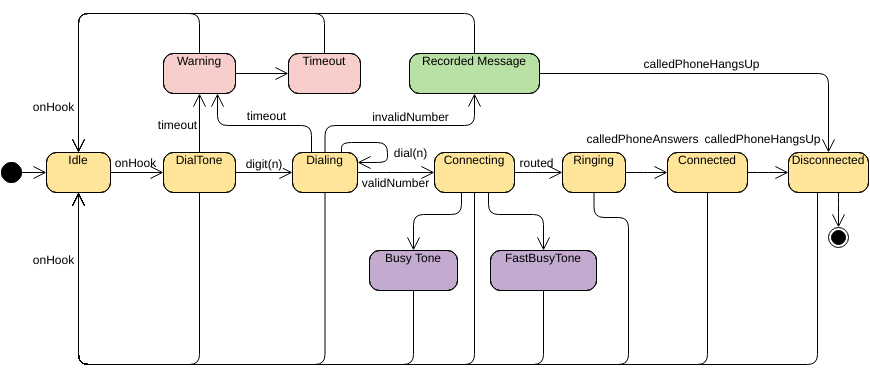
A state is a condition or situation in the course of an object’s life during which it satisfies some condition, performs some activity, or waits for some event. An object remains in one state for a limited period of time.
For example, a Heater in a home might be in any of four states: (1) Idle (waiting
for a command to start heating the house), (2) Activating (its gas is on, but it’s waiting to come up
to temperature), (3) Active (its gas and blower are both on), and (4) ShuttingDown (its gas is off but
its blower is on, flushing residual heat from the system).
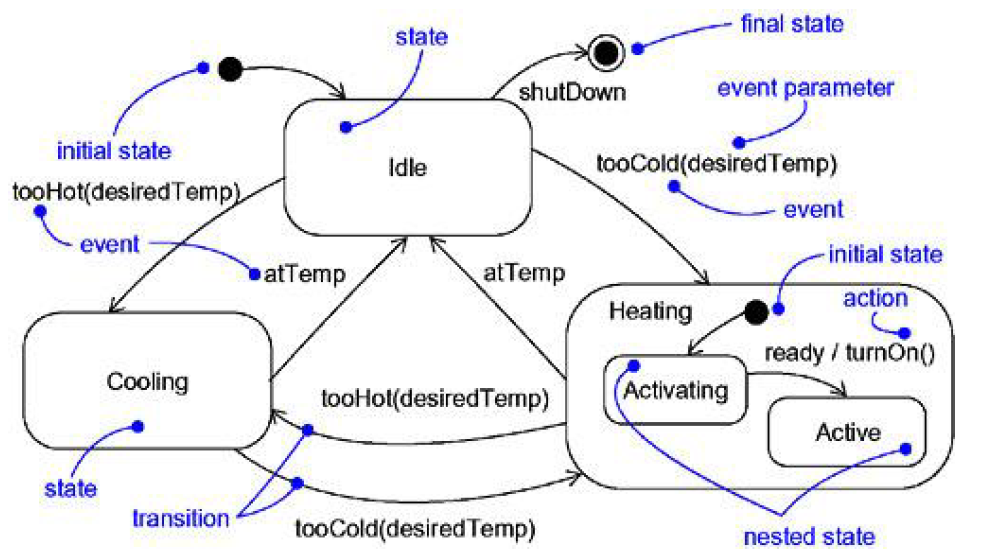
A transition is a relationship between two states indicating that an object in the first state will
perform certain actions and enter the second state when a specified event occurs and specified
conditions are satisfied. On such a change of state, the transition is said to fire. Until the transition
fires, the object is said to be in the source state; after it fires, it is said to be in the target state.
For example, a Heater might transition from the Idle to the Activating state when an event such
as tooCold (with the parameter desiredTemp) occurs.
Learn More State Machine Diagram by Examples
This post is also available in Deutsch, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.