What is a mind map? A mind map is a powerful visual tool that helps you organize information, ideas, and
Continue reading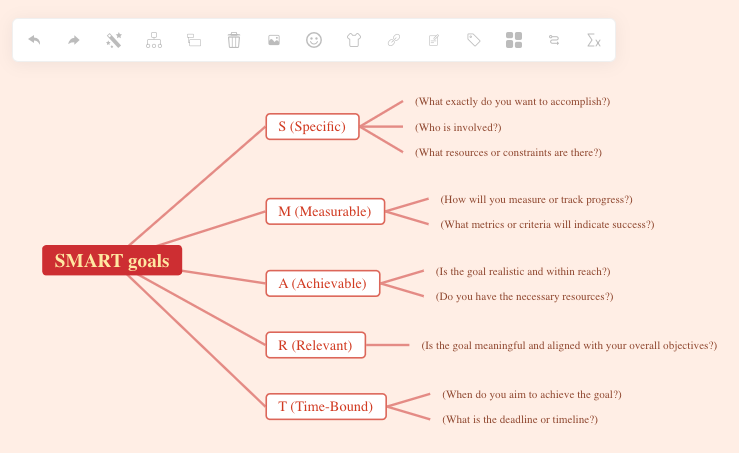
Learning one new thing everyday


What is a mind map? A mind map is a powerful visual tool that helps you organize information, ideas, and
Continue reading
Driving conversions with interactive PDF flipbooks is a powerful marketing strategy that can significantly impact your business’s bottom line. By
Continue reading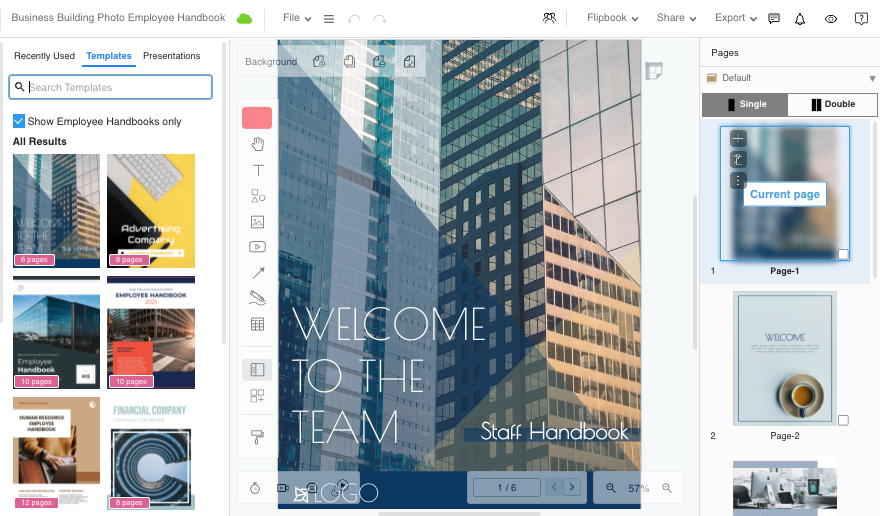
Publishing PDFs as interactive flipbooks offers several advantages that can greatly enhance your marketing efforts. Here are some key advantages
Continue reading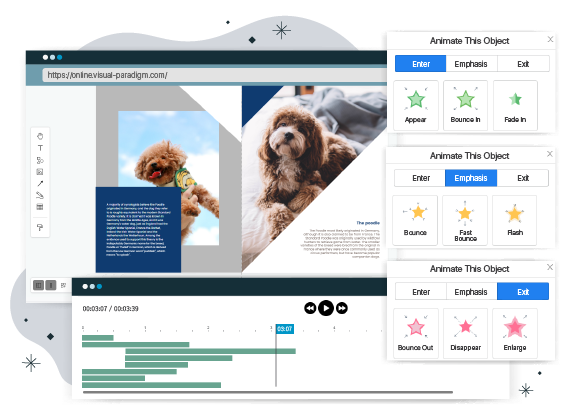
Introduction In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the need for visually captivating and interactive content is more pronounced than ever. As
Continue reading
Introduction Are you ready to revolutionize the way you present and showcase your content online? Look no further—Visual Paradigm Flipbook
Continue reading
Introduction In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing and content creation, the importance of multimedia integration within flipbooks cannot be
Continue reading
Introduction In the dynamic world of digital content, static PDFs no longer cut it. To truly captivate your audience and
Continue reading
Introduction Step into the future of content creation with Visual Paradigm’s Online Flipbook Maker. Gone are the days of static
Continue reading
What exactly is a digital flipbook? A digital flipbook serves as an engaging, brand-neutral HTML5 document for presenting content online.
Continue reading
Creating memorable brand experiences is essential for businesses to stand out in a sea of competition. Video marketing has emerged
Continue reading