Introduction
PEST analysis is a strategic tool used to understand the external factors that can impact an organization or industry. It stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. This case study will guide readers through the PEST analysis of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, explaining what PEST analysis is, when to use it, why it is important, and how to conduct it.

What is PEST Analysis?
PEST analysis is a framework that helps organizations identify and analyze the macro-environmental factors that can influence their operations and strategies. These factors are categorized into four main areas:
- Political: Government policies, regulations, and political stability.
- Economic: Economic conditions, trends, and factors that can impact the market.
- Social: Societal trends, consumer attitudes, and demographic factors.
- Technological: Technological advancements, innovations, and their impact on the industry.
When to Use PEST Analysis
PEST analysis is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Strategic Planning: When developing long-term strategies and understanding the external environment.
- Market Entry: When considering entering a new market or launching a new product.
- Risk Assessment: When identifying potential risks and opportunities in the external environment.
- Investment Decisions: When evaluating the feasibility of investments in a particular industry or market.
Why is PEST Analysis Important?
PEST analysis is important because it helps organizations:
- Identify Opportunities: Recognize potential opportunities for growth and expansion.
- Mitigate Risks: Identify and mitigate risks associated with external factors.
- Informed Decision-Making: Make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the external environment.
- Strategic Alignment: Align strategies with the external environment to ensure sustainability and competitiveness.
How to Conduct PEST Analysis
To conduct a PEST analysis, follow these steps:
- Identify the Factors: List the political, economic, social, and technological factors that can impact the industry or organization.
- Analyze the Impact: Assess the potential impact of each factor on the industry or organization.
- Evaluate the Significance: Determine the significance of each factor in terms of its potential impact and likelihood.
- Develop Strategies: Develop strategies to leverage opportunities and mitigate risks identified in the analysis.
PEST Analysis of the Electric Vehicle Industry
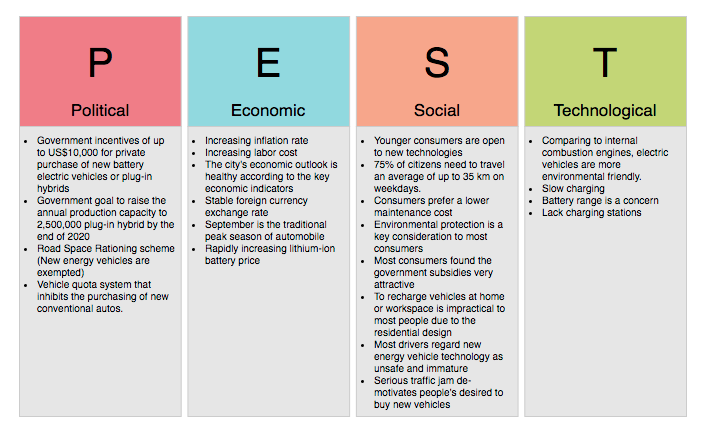
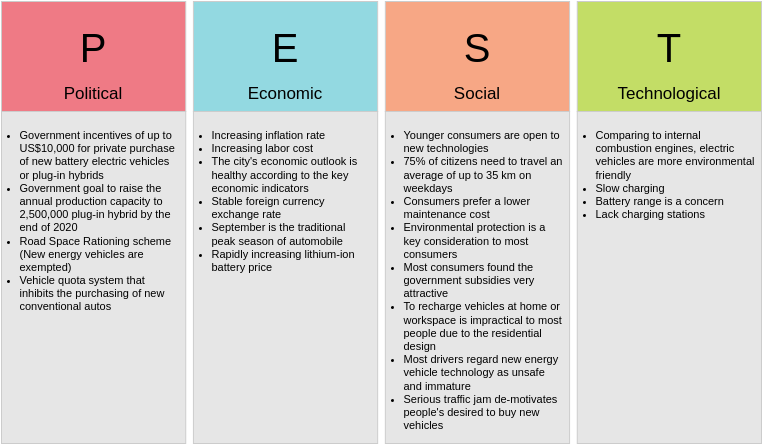
Political Factors:
- Government Incentives: The government offers incentives of up to US$10,000 for the private purchase of new battery electric vehicles or plug-in hybrids.
- Production Goals: The government aims to raise the annual production capacity to 2 million plug-in hybrids by the end of the decade.
- Road Space Rationing: New energy vehicles are exempt from the road space rationing scheme.
- Vehicle Quota System: There is a vehicle quota system that inhibits the purchasing of new conventional autos.
Economic Factors:
- Inflation and Labor Costs: Increasing inflation rates and labor costs can impact the production and pricing of EVs.
- Economic Outlook: The city’s economic outlook is healthy, which is positive for the EV market.
- Foreign Currency Exchange: Stable foreign currency exchange rates can benefit the import and export of EV components.
- Automotive Market: September is the traditional peak season for automobiles, which can boost EV sales.
- Battery Prices: Rapidly increasing lithium-ion battery prices can affect the cost of EVs.
Social Factors:
- Consumer Preferences: Younger consumers are open to new technologies, and 75% of citizens need to travel an average of up to 35 km on weekdays.
- Maintenance Costs: Consumers prefer a lower maintenance cost, and environmental protection is a significant consideration for most consumers.
- Government Subsidies: Most consumers are aware of the government subsidies for EVs.
- Charging Infrastructure: The lack of charging stations is a concern for consumers.
- Technology Perception: Most drivers regard new energy vehicle technology as unsafe and immature, which can hinder EV adoption.
Technological Factors:
- Environmental Friendliness: Compared to internal combustion engines, electric vehicles are more environmentally friendly.
- Silent Operation: EVs operate silently, which is a advantage for consumers.
- Battery Range: Battery range is a concern for consumers, as it can limit the distance they can travel.
- Charging Stations: The lack of charging stations can hinder the adoption of EVs.
Applying the Findings of PEST Analysis to the Electric Vehicle Industry
Conducting a PEST analysis provides valuable insights into the external environment affecting the electric vehicle (EV) industry. To apply these findings effectively, organizations need to develop strategies that leverage opportunities and mitigate risks. Here’s how to apply the findings from the PEST analysis:
Political Factors
- Government Incentives:
- Action: Promote government incentives in marketing campaigns to attract potential buyers.
- Strategy: Partner with government agencies to offer bundled incentives and financing options.
- Production Goals:
- Action: Invest in expanding production capacities to meet government targets.
- Strategy: Collaborate with suppliers to ensure a steady supply chain and scale production efficiently.
- Road Space Rationing:
- Action: Highlight the exemption from road space rationing in advertising to emphasize the convenience of EVs.
- Strategy: Develop targeted marketing campaigns for urban areas where road space rationing is a significant issue.
- Vehicle Quota System:
- Action: Educate consumers about the benefits of EVs in bypassing the vehicle quota system.
- Strategy: Offer special deals and promotions to consumers who are affected by the quota system.
Economic Factors
- Inflation and Labor Costs:
- Action: Monitor economic indicators and adjust pricing strategies accordingly.
- Strategy: Implement cost-saving measures and improve operational efficiency to offset increasing labor costs.
- Economic Outlook:
- Action: Leverage the healthy economic outlook to invest in research and development.
- Strategy: Expand market reach and introduce new EV models to capitalize on the positive economic conditions.
- Foreign Currency Exchange:
- Action: Hedge against currency fluctuations to stabilize costs.
- Strategy: Diversify the supply chain to reduce dependency on a single currency.
- Automotive Market:
- Action: Plan marketing and sales strategies around peak seasons.
- Strategy: Offer seasonal promotions and discounts to boost sales during the traditional peak season.
- Battery Prices:
- Action: Invest in battery technology research to develop more cost-effective solutions.
- Strategy: Secure long-term contracts with battery suppliers to lock in prices and ensure a stable supply.
Social Factors
- Consumer Preferences:
- Action: Tailor marketing efforts to appeal to younger, tech-savvy consumers.
- Strategy: Develop EV models with advanced features and lower maintenance costs to attract environmentally conscious consumers.
- Maintenance Costs:
- Action: Highlight the lower maintenance costs of EVs in marketing materials.
- Strategy: Offer maintenance packages and warranties to reassure consumers about long-term costs.
- Government Subsidies:
- Action: Ensure consumers are aware of available subsidies through targeted advertising.
- Strategy: Partner with financial institutions to offer subsidy-inclusive financing options.
- Charging Infrastructure:
- Action: Advocate for the development of more charging stations.
- Strategy: Invest in building a network of charging stations or partner with existing providers to improve accessibility.
- Technology Perception:
- Action: Address consumer concerns about the safety and maturity of EV technology.
- Strategy: Conduct public awareness campaigns and demonstrate the reliability and safety of EVs through test drives and reviews.
Technological Factors
- Environmental Friendliness:
- Action: Emphasize the environmental benefits of EVs in all marketing communications.
- Strategy: Develop eco-friendly branding and partner with environmental organizations to enhance credibility.
- Silent Operation:
- Action: Highlight the silent operation of EVs as a unique selling point.
- Strategy: Create advertising campaigns that showcase the quiet and smooth driving experience of EVs.
- Battery Range:
- Action: Invest in improving battery technology to increase range.
- Strategy: Offer EV models with different battery range options to cater to various consumer needs.
- Charging Stations:
- Action: Collaborate with charging station providers to expand the network.
- Strategy: Develop apps and platforms that help consumers locate and use charging stations easily.
Conclusion
PEST analysis is a valuable tool for understanding the external environment and its impact on the electric vehicle industry. By identifying and analyzing the political, economic, social, and technological factors, organizations can develop strategies to leverage opportunities and mitigate risks. This case study provides a comprehensive guide to conducting PEST analysis and highlights its importance in strategic planning and decision-making.
Applying the findings of a PEST analysis involves developing strategic actions and initiatives that address the identified factors. By leveraging opportunities and mitigating risks, organizations in the electric vehicle industry can enhance their competitiveness, attract more consumers, and contribute to a sustainable future. This comprehensive approach ensures that the EV industry can thrive in a dynamic and ever-changing external environment.