Introduction Use Case Analysis is a critical technique in software engineering and systems analysis that helps in understanding, capturing, and
Continue reading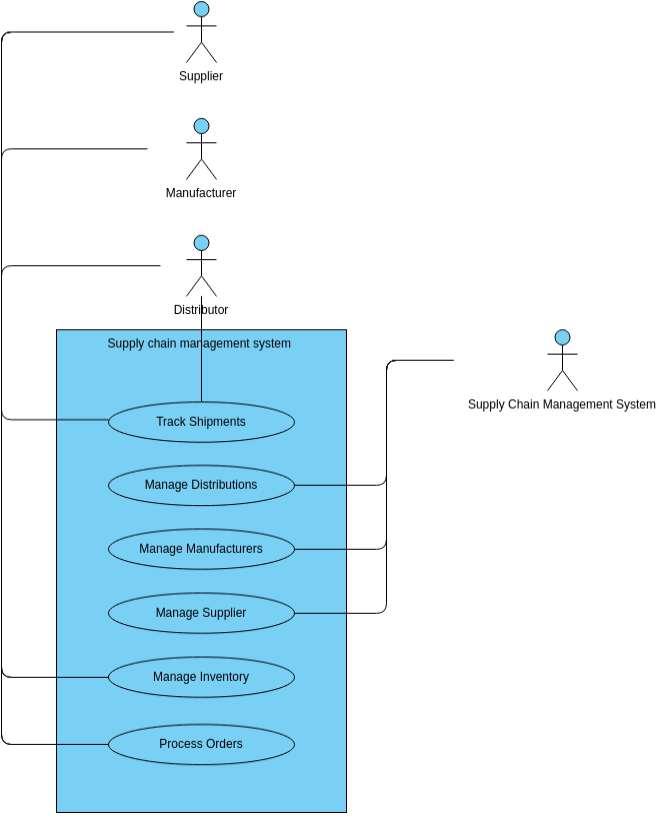
Learning one new thing everyday


Introduction Use Case Analysis is a critical technique in software engineering and systems analysis that helps in understanding, capturing, and
Continue reading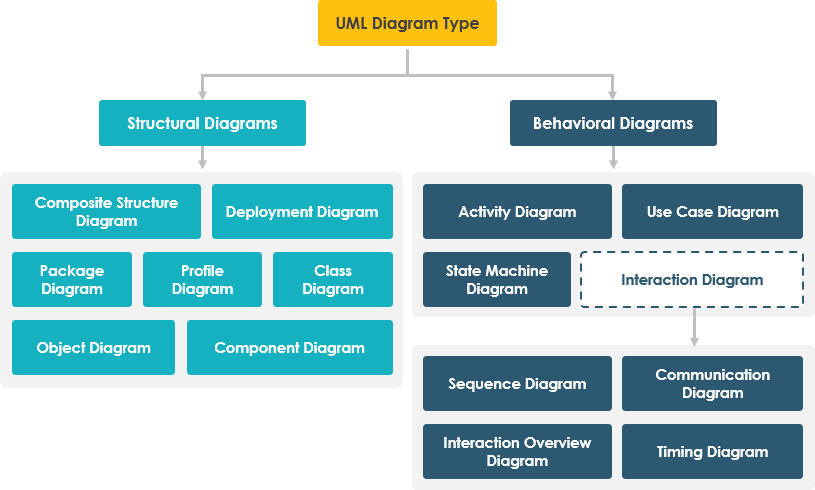
Purpose of UML Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standard language for specifying, visualizing, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of
Continue reading
Introduction Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams are essential tools in software engineering, providing a standardized way to visualize the design
Continue reading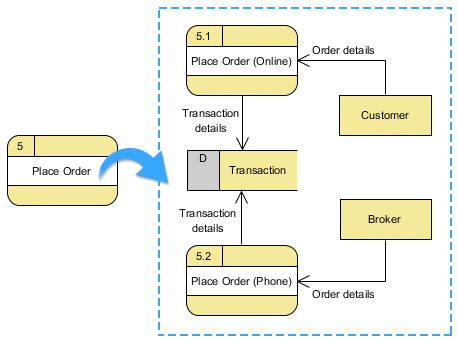
Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) have been a cornerstone in system analysis and design since the 1970s, celebrated for their clarity
Continue reading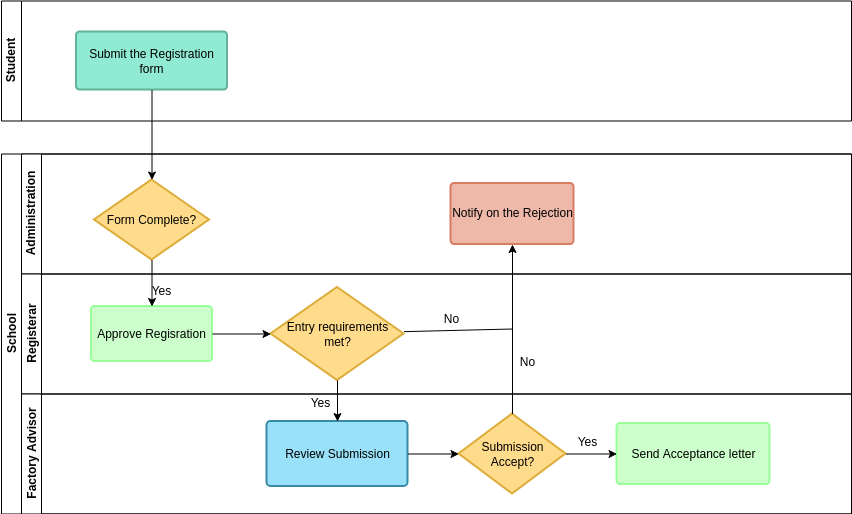
Introduction Swimlane activity diagrams are a type of UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagram used to model the workflow of a
Continue reading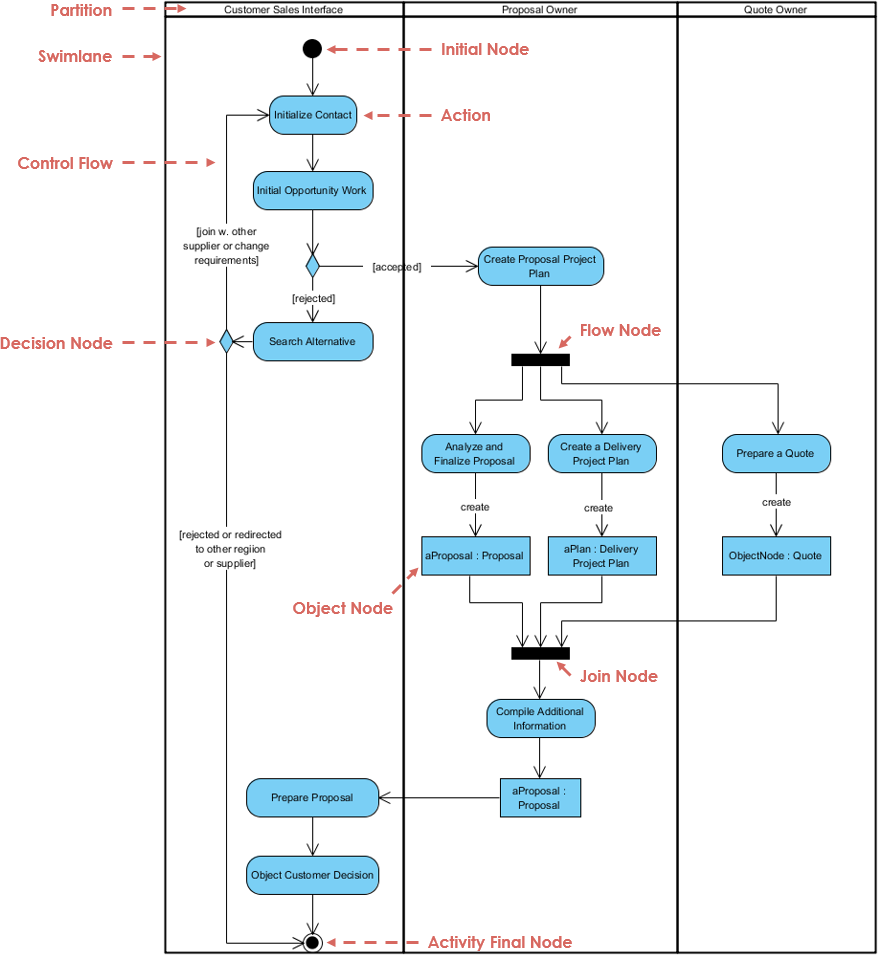
Introduction Swimlane activity diagrams are a type of UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagram used to model the workflow of a
Continue reading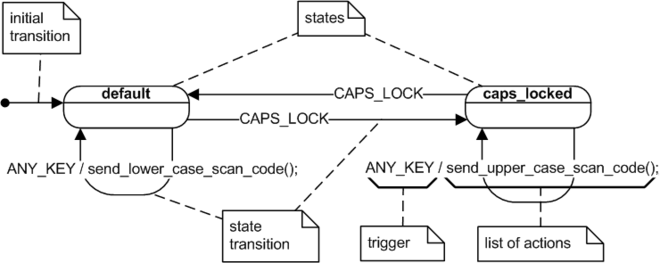
Unified Modeling Language (UML) State Machine Diagrams are powerful tools for modeling the dynamic behavior of systems. They illustrate the
Continue reading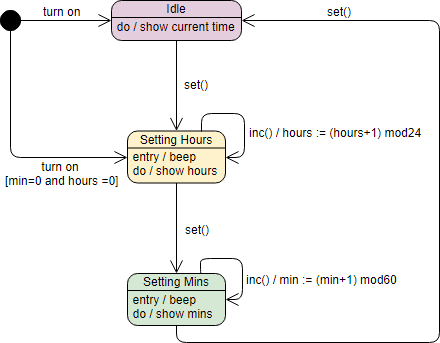
UML State Charts, also known as State Machine Diagrams, are a type of behavioral diagram in the Unified Modeling Language
Continue reading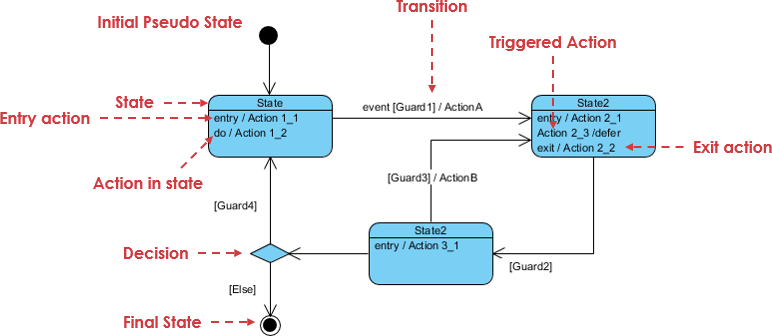
State Machine Diagrams are a crucial part of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), used to model the dynamic behavior of
Continue reading
Unified Modeling Language (UML) Timing Diagrams are a type of interaction diagram that focuses on the timing constraints of objects
Continue reading