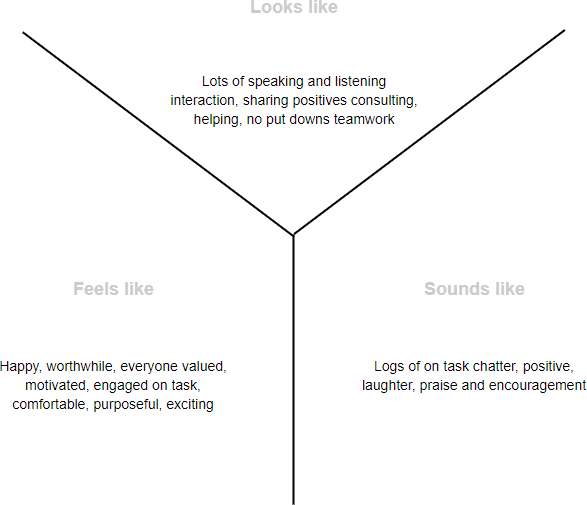
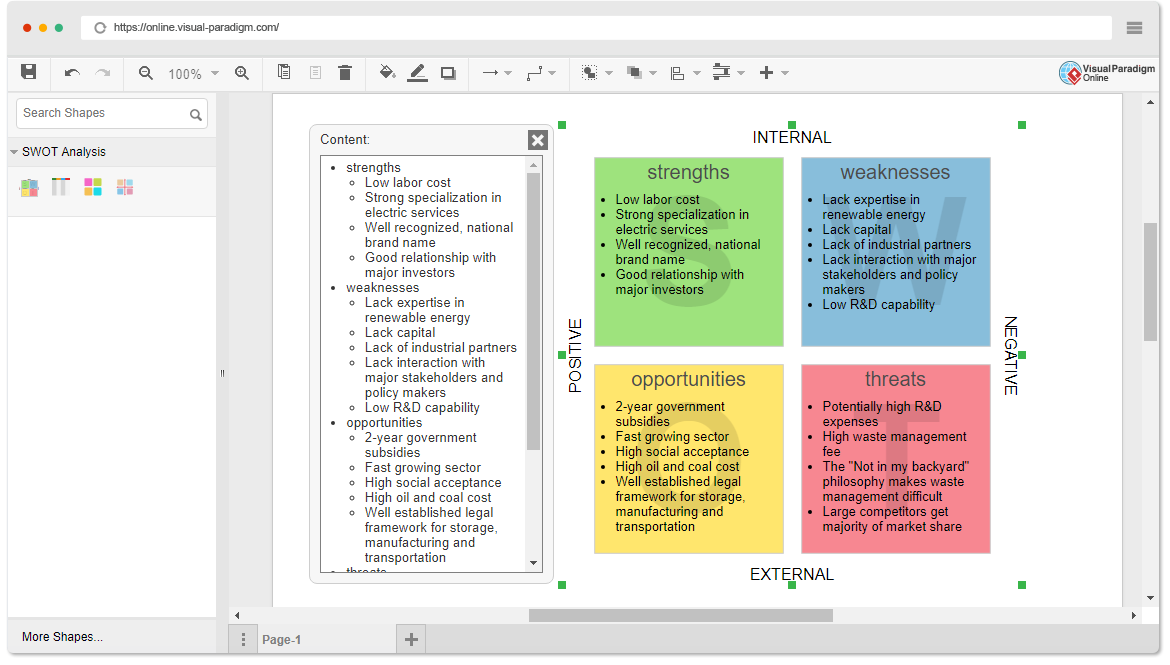
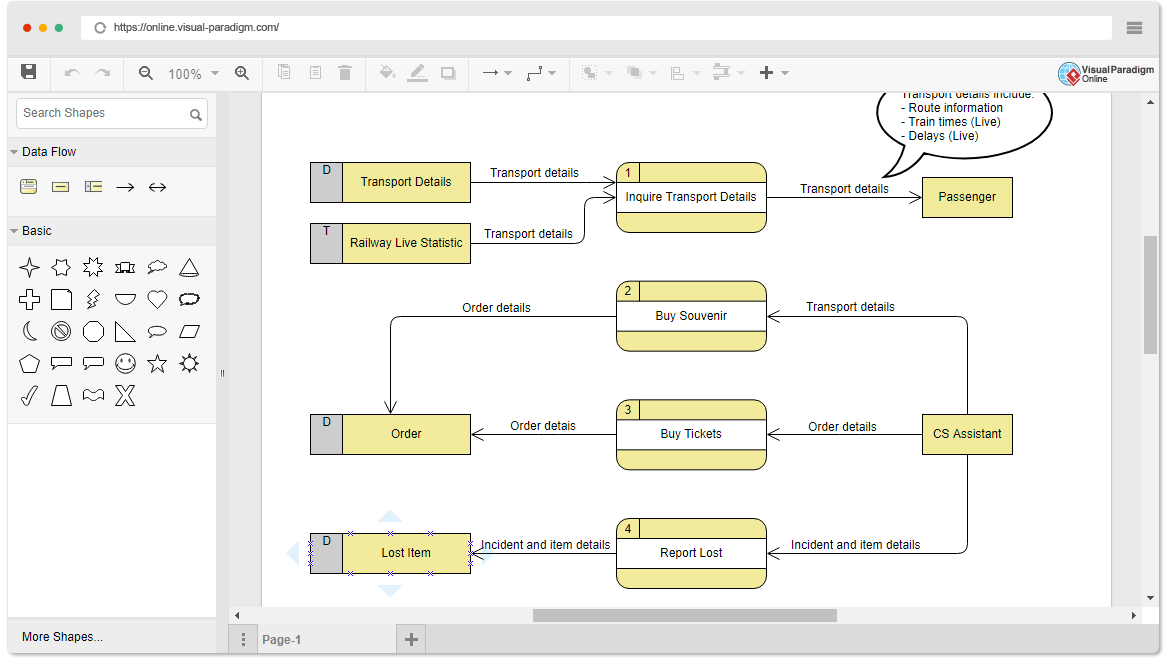
Both T-charts and Y-charts help to graphically organize and record ideas, feelings and information, while identifying and focusing on what teachers / students already know, understand, value and can do. It enables students / teachers / teachers to compare and contrast ideas, feelings and information in various context.
Continue reading