Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standard visual modeling language used to specify, visualize, construct, and document software systems. It
Continue reading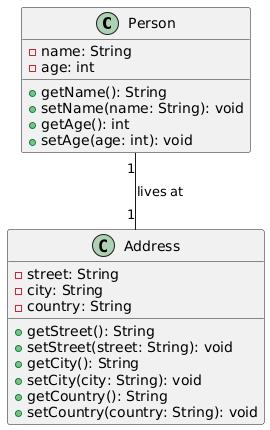
Learning one new thing everyday


Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standard visual modeling language used to specify, visualize, construct, and document software systems. It
Continue readingIn the dynamic landscape of strategic planning, where clarity and creativity coexist, finding a tool that encapsulates both is indispensable.
Continue reading
In the realm of strategic planning, finding a tool that not only organizes thoughts but also brings creativity to the
Continue reading
In the expansive landscape of strategic planning, where ideas are seeds waiting to sprout, finding the right cultivation tool is
Continue reading
In the dynamic landscape of strategic planning, the ability to organize thoughts and ideas is paramount. Enter the Fishbone Diagram,
Continue reading
In the realm of planning and organization, having a structured and organized approach is essential for success. In this blog
Continue reading
Interactive flipbooks have emerged as a powerful tool for boosting conversion rates in digital marketing. By incorporating interactive elements and
Continue reading
In the world of planning and organization, having a clear structure and well-defined roles is essential for success. In this
Continue reading
Embarking on the journey of tracing your family history can be an exciting and fulfilling endeavor. To navigate through the
Continue reading
In the intricate landscape of planning and strategy, finding a reliable map is crucial to navigate the complexities and uncertainties
Continue reading