In the era of digital communication, the ability to present information in an engaging and visually appealing manner is essential.
Continue reading
Learning one new thing everyday

In the era of digital communication, the ability to present information in an engaging and visually appealing manner is essential.
Continue reading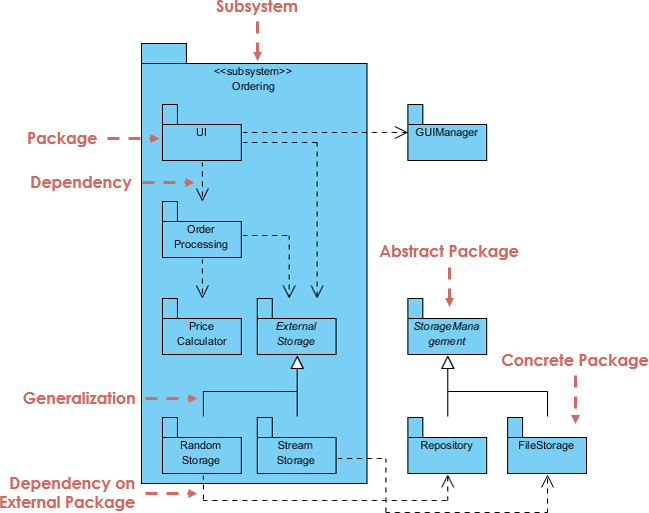
A UML Package Diagram is used to organize and group parts of a system into packages, making it easier to
Continue reading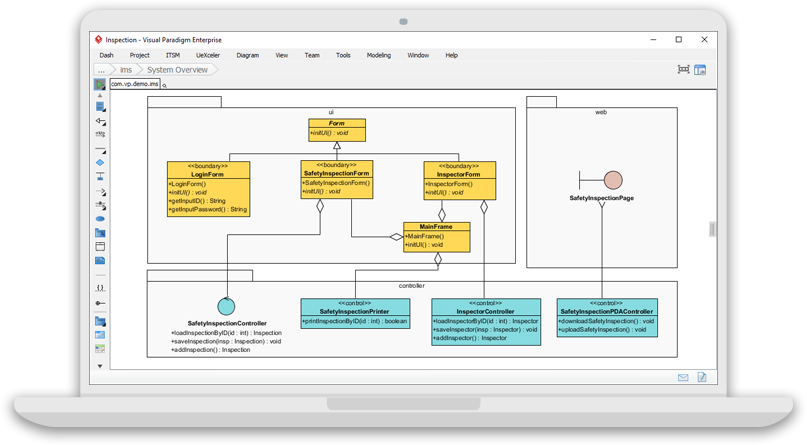
Introduction Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standardized modeling language that provides a way to visualize the design of software
Continue reading
Introduction Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation of business workflows that helps stakeholders easily understand and
Continue reading
Visual Paradigm’s BPMN tool is a powerful online solution for creating, analyzing, and improving business processes. To help you get
Continue readingIn software development, visual modeling techniques are essential for understanding and documenting processes. Activity diagrams and sequence diagrams are two
Continue readingIntroduction Use cases, sequence diagrams, and activity diagrams are all tools used in software engineering to model and understand the
Continue readingIntroduction Sequence diagrams are a crucial part of visualizing and understanding dynamic aspects of a system. They show how objects
Continue reading
Introduction The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a widely used visual language for modeling object-oriented systems. UML helps to understand,
Continue reading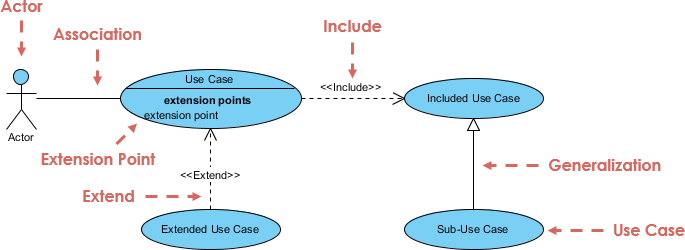
Introduction Use cases are a vital tool in software development, serving as a primary means of capturing and communicating system
Continue reading