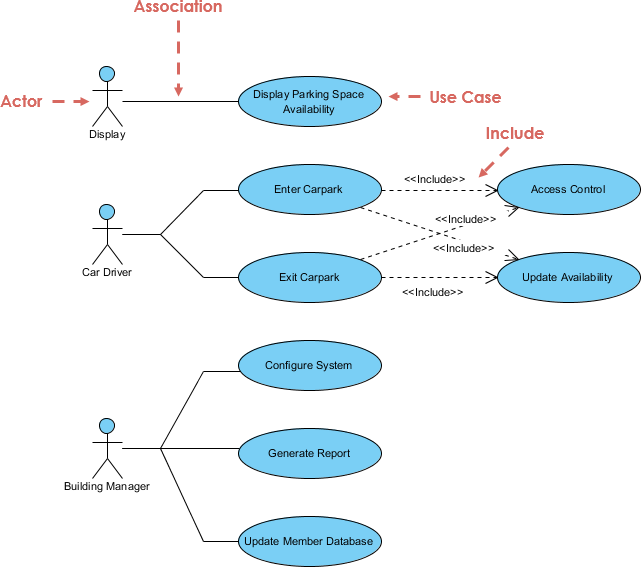
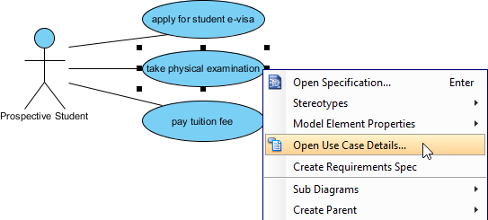
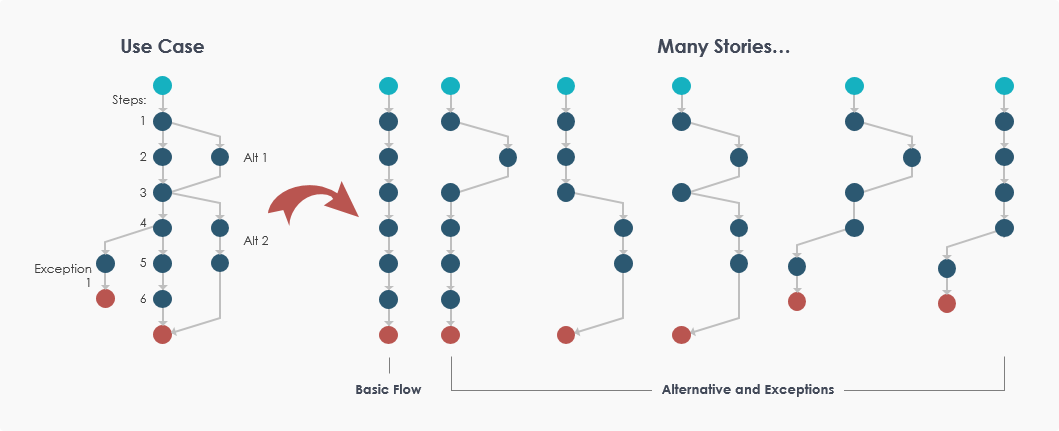
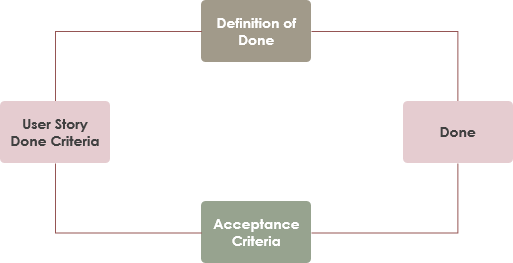
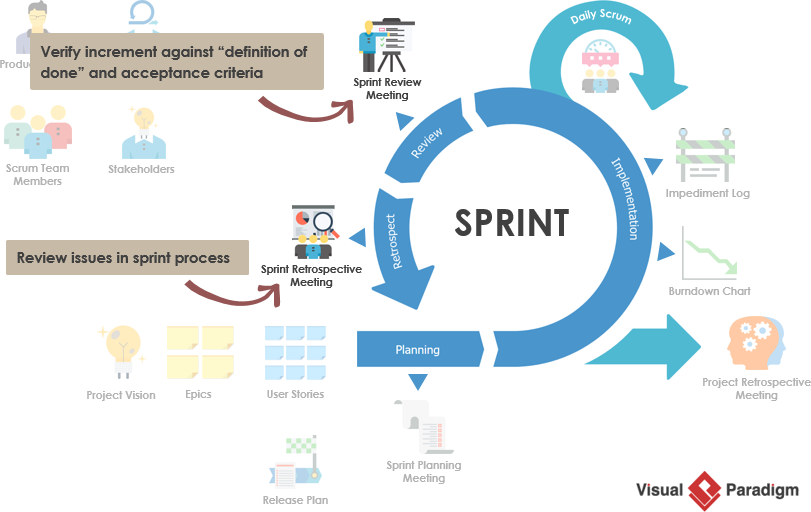
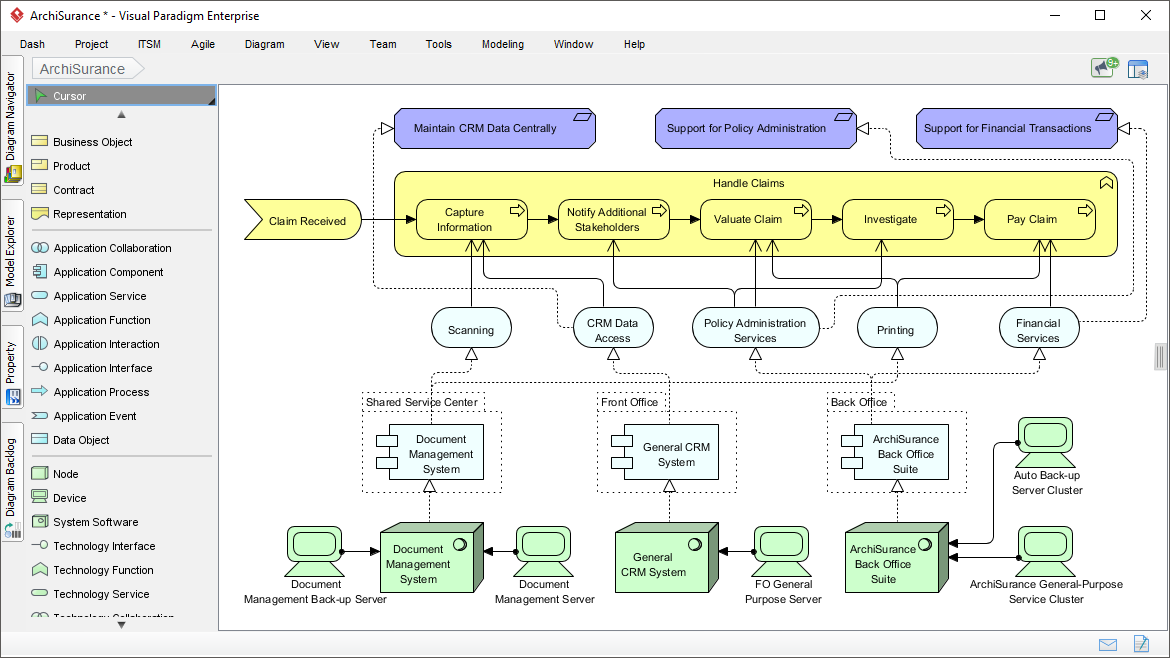
In software development , the usual “estimation” includes a quantitative evaluation of the work required to perform a given development task; this is usually expressed in terms of duration (hour / day) or estimated unit (story point). The purpose is to consolidate a number of such individual estimates in order to obtain an indication of the overall duration, work or cost of the software project.
Continue reading