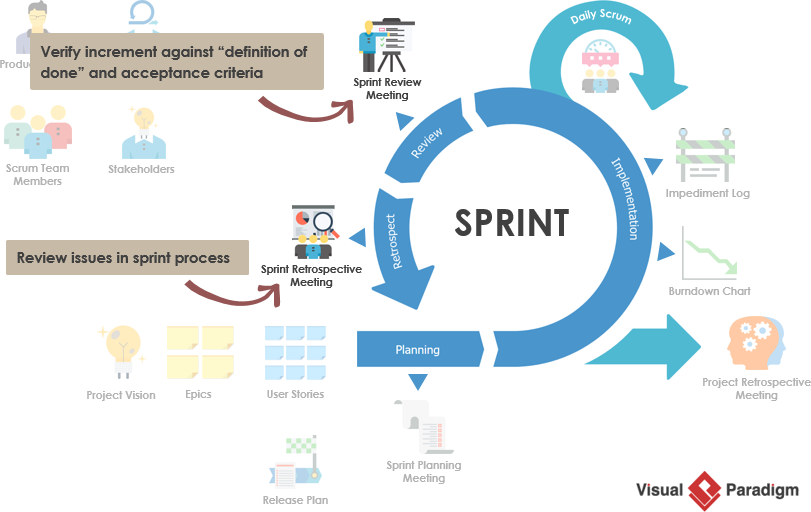
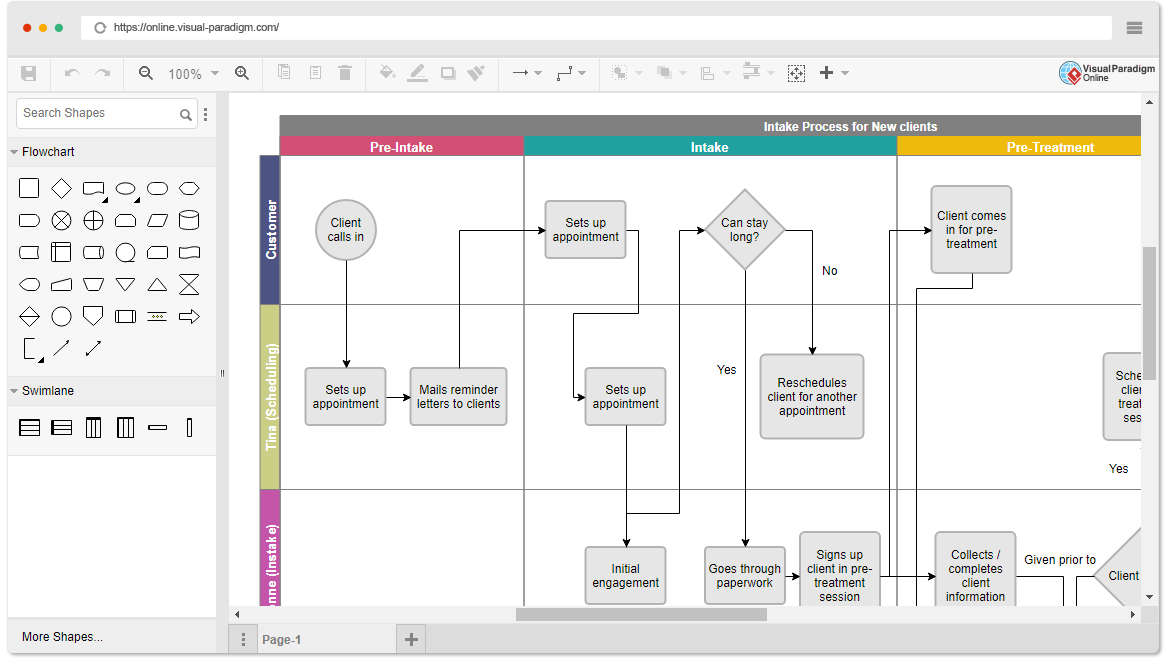
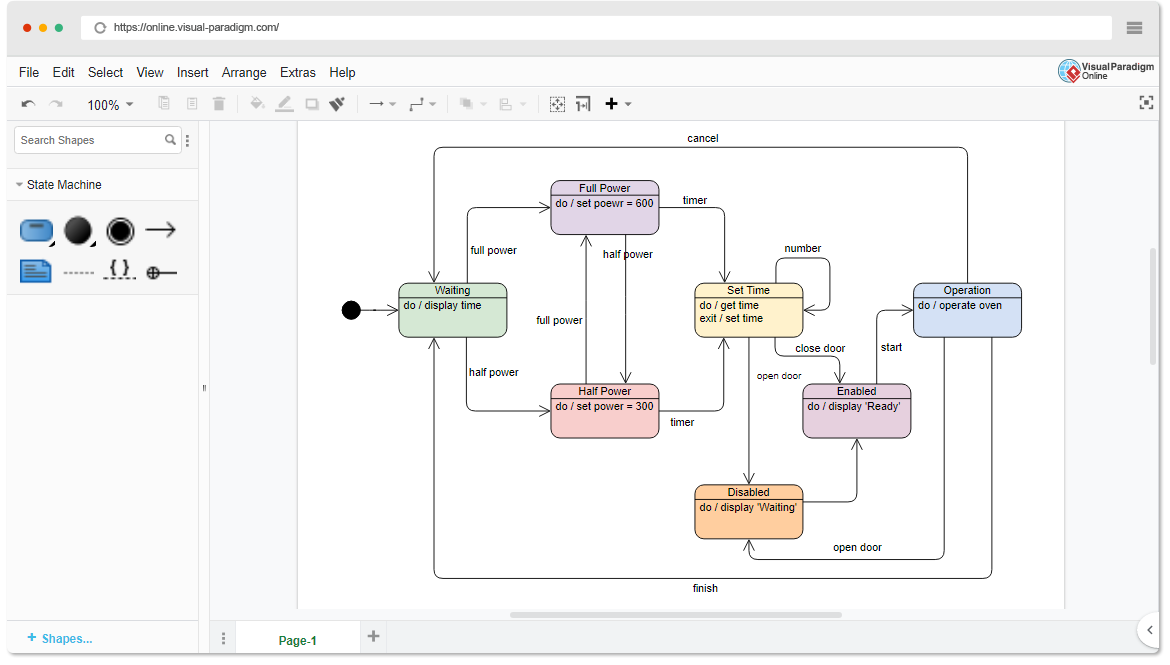
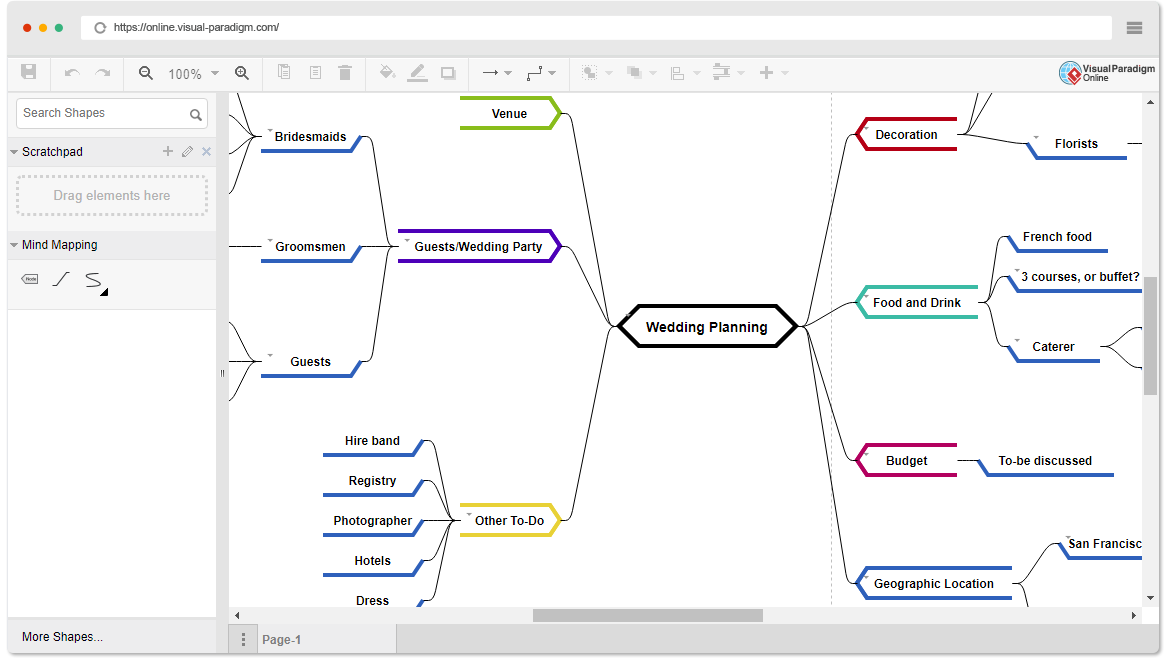
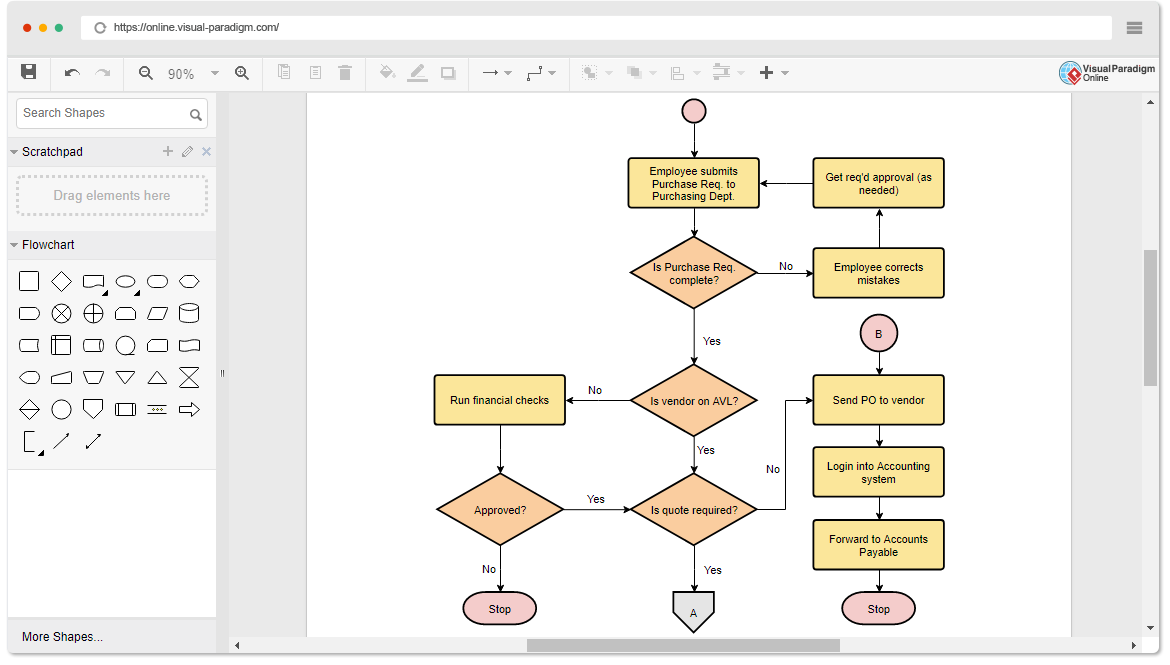
Each sprint ends with a two-part sprint review meeting. Such a meeting starts with a customer review and demonstration and ends with the team retrospective. Both of these components occur on the last day of the sprint. The Sprint Review focuses on the “inspect” and “adapt” of the increment (Potentially shippable), while the Sprint Retrospective give more focus on the “inspect” and “adapt” of the process of the sprint.
Continue reading