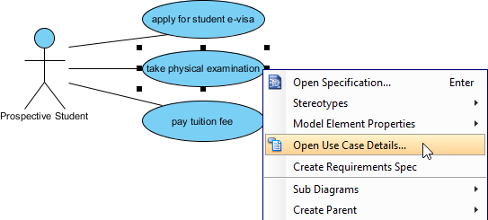
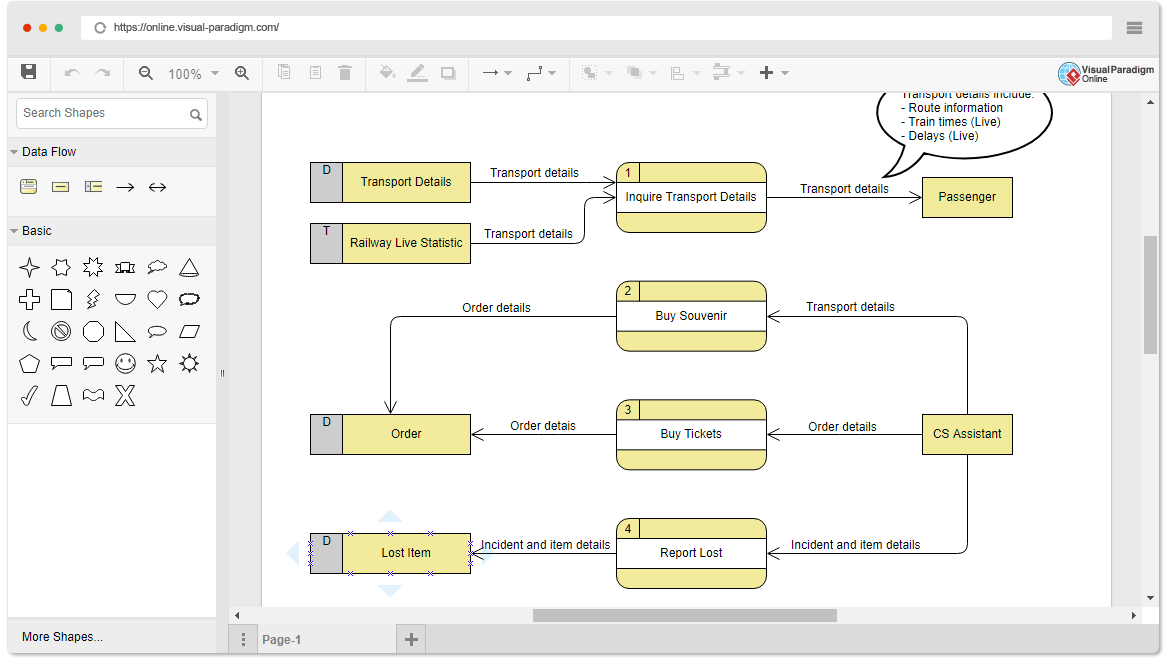
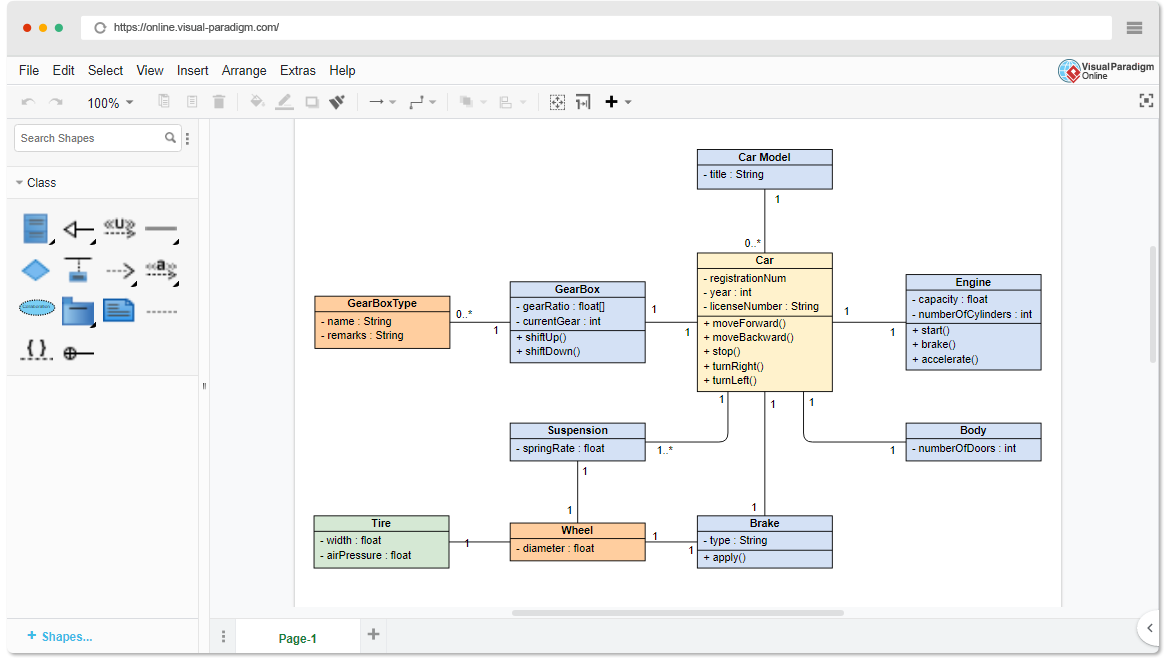
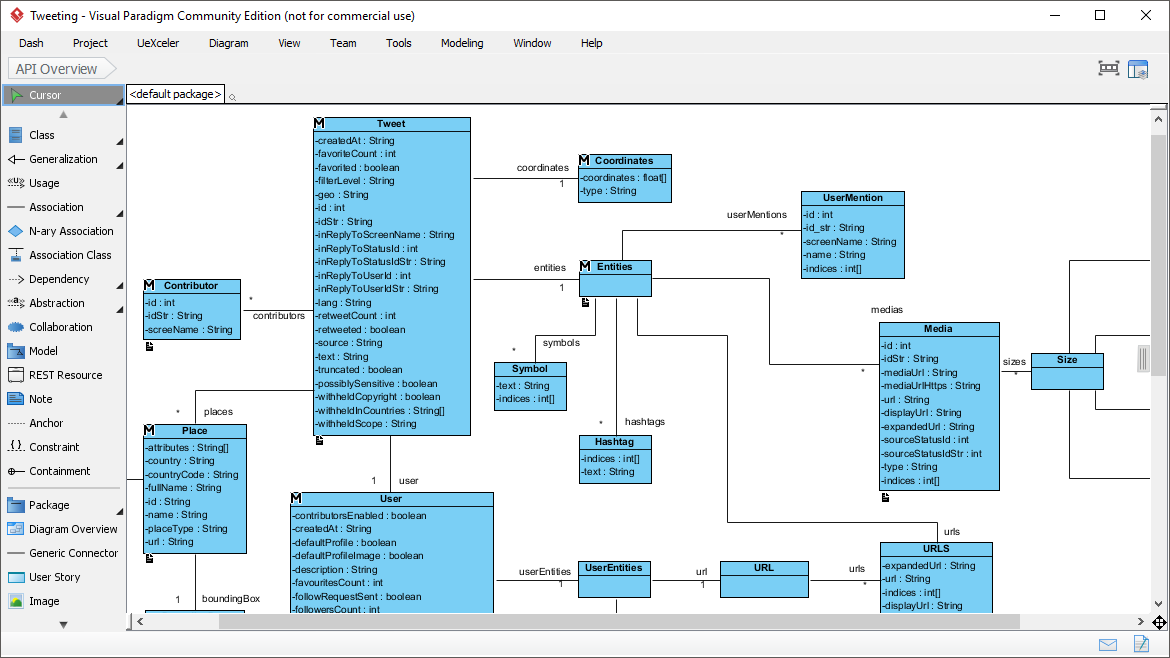
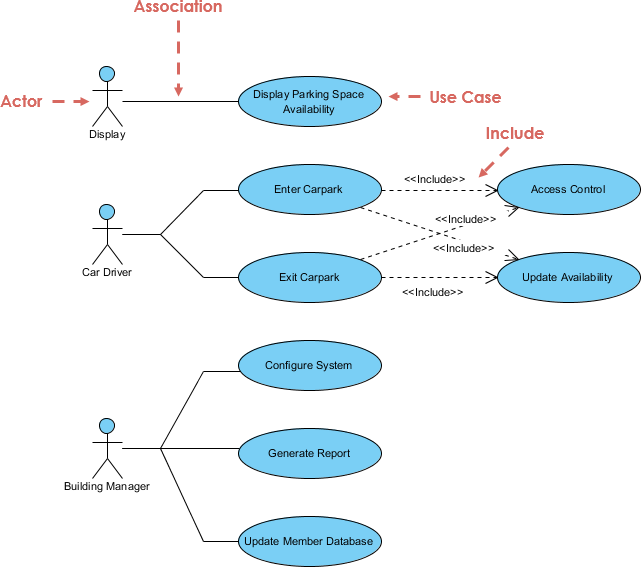
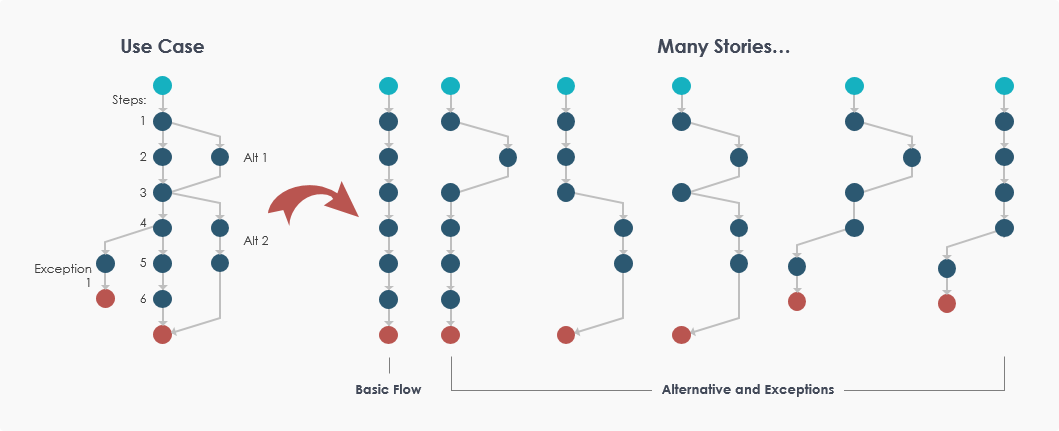
A use case is a requirements capture and documentation technique that can be written in plain text to describe in a narrative manner the actions and interactions of participants using the system. Finally, the functionality of the system should satisfy the purpose for which stakeholders use the system.
Continue reading