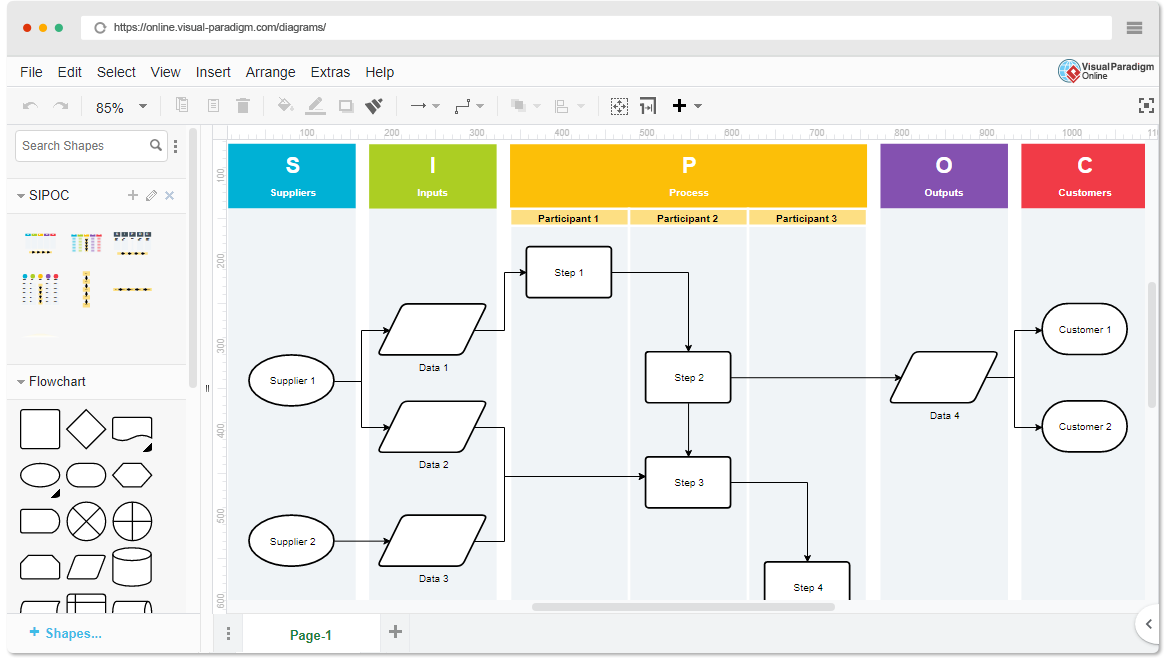
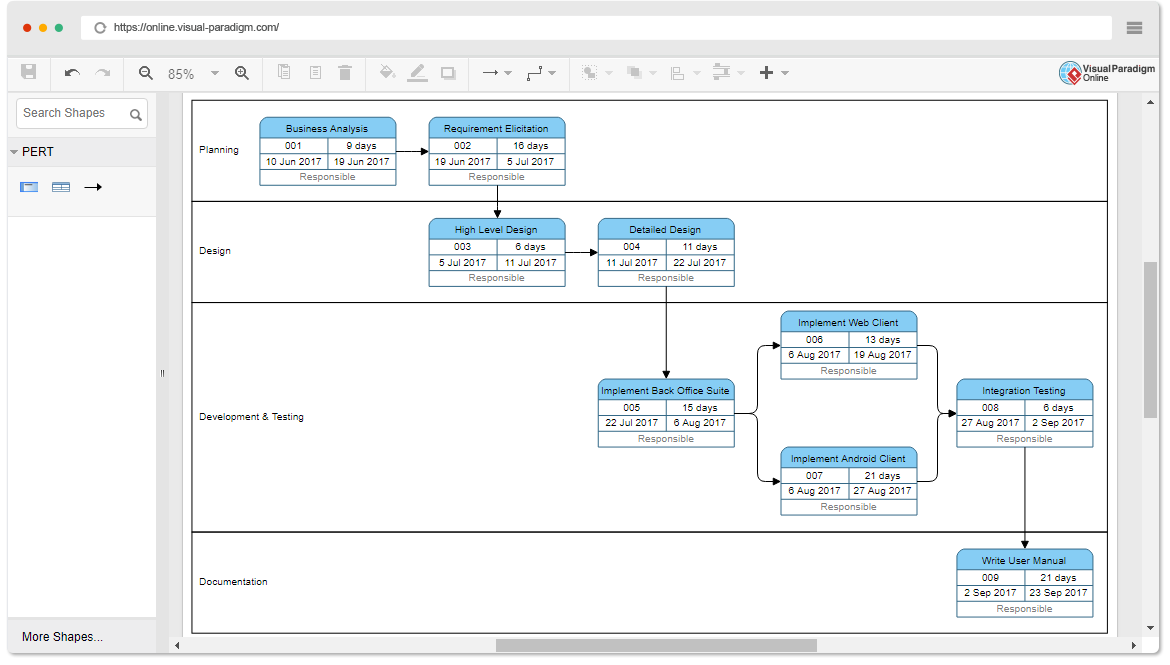
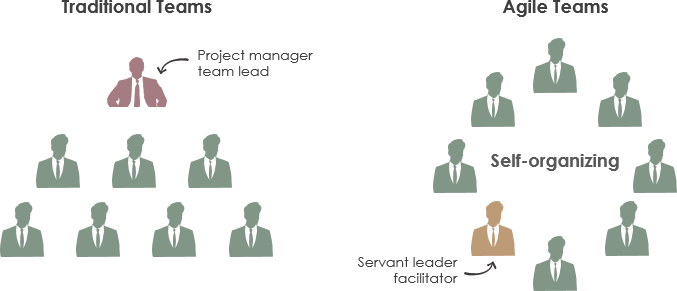
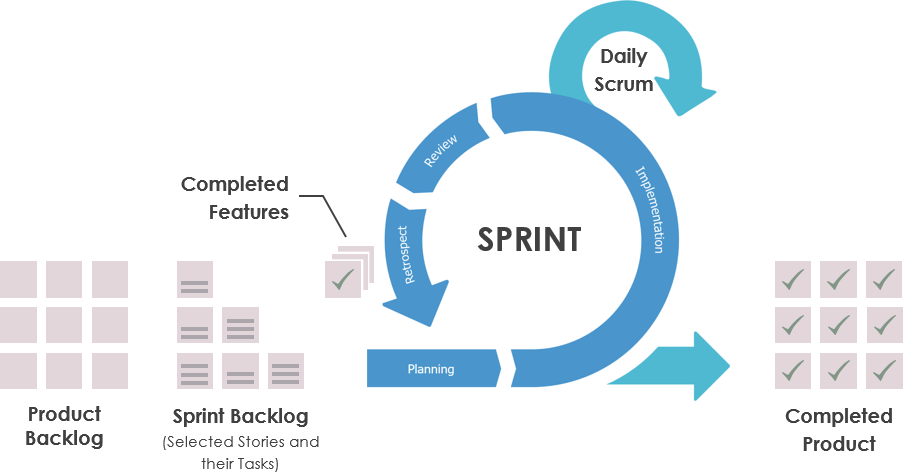
The acronym SIPOC stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customer. Using information from these five areas creates a process map that gives a high-level overview of a Six Sigma project. To create a SIPOC diagram, you have to specify the five main activities of the process and identify the potential suppliers, inputs, outputs, and customers.
Continue reading