Phân tích khoảng cách bao gồm việc so sánh hiệu suất thực tế với hiệu suất tiềm năng. Ví dụ, nếu một công ty không tận dụng tối đa các nguồn lực hiện có, họ có thể hoạt động dưới mức tiềm năng lý tưởng. Nói cách khác, phân tích khoảng cách là quá trình mà mọi người sử dụng để kiểm tra trạng thái hiện tại (quy trình hiện trạng) so với trạng thái mong muốn (quy trình tương lai) của một công ty.
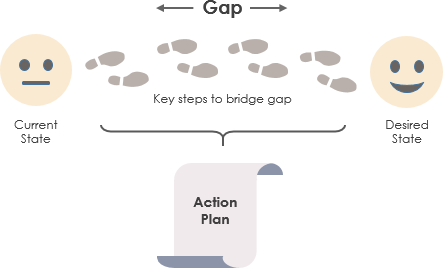
Một kỹ thuật hiệu quả để biến tầm nhìn thành kết quả là phát triển và điền thông tin vào các sơ đồ BPMN hiện trạng (As-Is) và tương lai (To-Be). Sơ đồ hiện trạng mô tả trạng thái hiện tại của quy trình, văn hóa và năng lực của tổ chức. Sơ đồ tương lai mô tả trạng thái tương lai; nói cách khác, cách mà quy trình, văn hóa và năng lực của tổ chức sẽ xuất hiện trong tương lai. Việc nghiên cứu quy trình hiện trạng và tương lai giúp xác định sự khác biệt giữa trạng thái kinh doanh hiện tại và mục tiêu, được gọi là khoảng cách, một phần quan trọng trong bất kỳ sáng kiến tái cấu trúc/cải thiện quy trình kinh doanh nào.
Quy trình hiện trạng / tương lai là gì?
Trạng thái hiện trạng của một quy trình là trạng thái “hiện tại”. Đó là cách hoạt động của quy trình trước khi bạn thực hiện bất kỳ thay đổi hoặc cải tiến nào. Ngược lại, quy trình tương lai là trạng thái của tương lai.
Quy trình “hiện trạng” cho phép bạn có cái nhìn chính xác về cách mà quy trình hiện hoạt động. Khi đã hiểu rõ quy trình như thế nào, bạn có thể phân tích nó và đề xuất những cải tiến nhất định. BPMN là ký hiệu được sử dụng phổ biến nhất để tài liệu hóa phân tích khoảng cách.
Khoảng cách đề cập đến khoảng cách giữa “nơi chúng ta đang ở” (trạng thái hiện tại) và “nơi chúng ta muốn đến” (trạng thái mục tiêu). Một công ty có thể xác định trạng thái hiện tại của mình — bằng cách đo lường thời gian, tiền bạc và lao động — và so sánh nó với trạng thái mục tiêu. Bằng cách xác định và phân tích những khoảng cách này, ban quản lý có thể tạo ra kế hoạch hành động để đưa tổ chức tiến lên và lấp đầy những khoảng trống về hiệu suất.
Sơ đồ quy trình kinh doanh là gì?
Chuẩn ký hiệu mô hình hóa quy trình kinh doanh (BPMN) là một phương pháp để mô hình hóa quy trình kinh doanh. Nó hỗ trợ việc xác định các quy trình kinh doanh dưới dạng ký hiệu đồ họa (Sơ đồ Quy trình Kinh doanh) dựa trên khái niệm của sơ đồ hoạt động trong Ngôn ngữ Mô hình Hóa Thống nhất (UML). BPMN cung cấp cho các doanh nghiệp khả năng hiểu được các quy trình nội bộ của họ dưới dạng ký hiệu đồ họa và giúp các tổ chức có thể truyền đạt các quy trình đó một cách tiêu chuẩn. Điều này sẽ đảm bảo rằng tất cả các bên liên quan trong kinh doanh, chuyên gia CNTT và các thành viên khác trong doanh nghiệp giao tiếp hiệu quả, đồng thời giúp các tổ chức đối phó với sự thay đổi một cách rõ ràng, nhanh chóng và tốt hơn.

Ví dụ Phân tích Khoảng cách BPMN — Cửa hàng trực tuyến
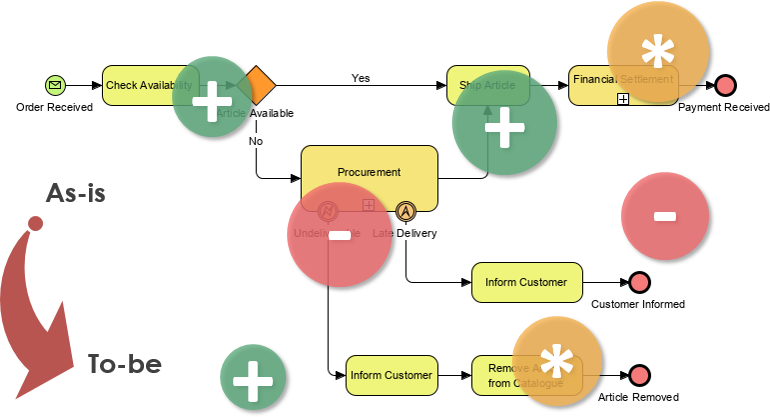
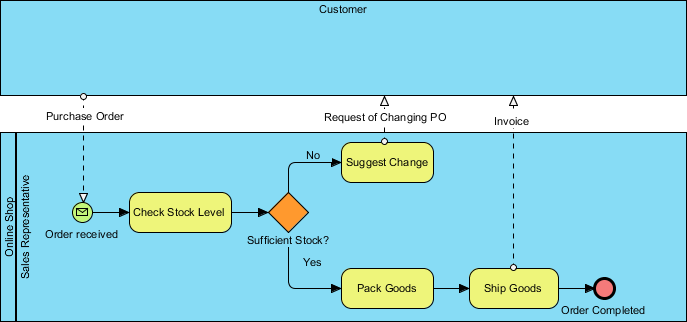
Ví dụ mà chúng tôi sắp trình bày là về một cửa hàng trực tuyến bán hàng hóa. Quy trình bắt đầu khi đại diện bán hàng nhận được đơn đặt hàng từ khách hàng và tiến hành kiểm tra mức tồn kho. Nếu có đủ hàng để đáp ứng đơn đặt hàng, đại diện bán hàng sẽ đóng gói chúng. Quy trình kết thúc bằng việc vận chuyển hàng đi kèm với hóa đơn. Trong trường hợp tồn kho không đủ, đại diện bán hàng sẽ đề nghị khách hàng sửa đổi đơn đặt hàng.
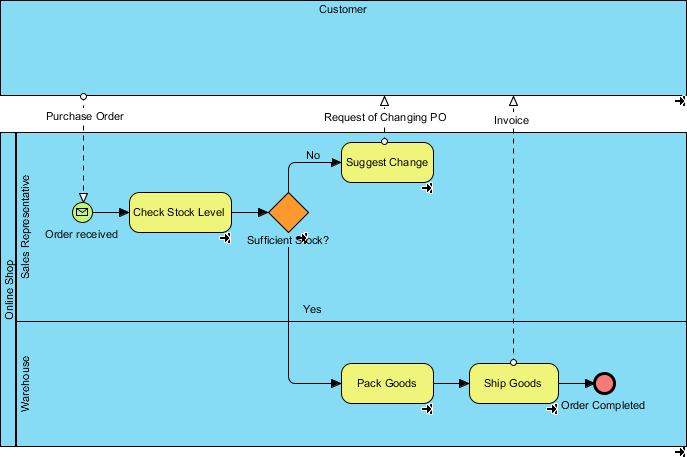
Nâng cao quy trình hiện trạng với quy trình tương lai
Giả sử doanh nghiệp của chúng ta đã phát triển đến mức mà bây giờ cần có một kho để giữ cho mức tồn kho luôn ở mức hợp lý. Vì vậy, chúng ta đang tìm cách cải thiện quy trình hiện tại (hiện trạng) bằng cách phân bổ các nguồn lực mới — kho lưu trữ cho cửa hàng trực tuyến nhằm giảm bớt khối lượng công việc nặng của các đại diện bán hàng và quản lý tồn kho tốt hơn.
Tài nguyên khác:
- Cách phát triển quy trình kinh doanh Hiện trạng và Tương lai với Visual Paradigm?
- Thiết kế quy trình kinh doanh với phần mềm BPMN mạnh mẽ
- BPMN là gì?
- Tại sao cần mô hình hóa UML?
- BPMN: Điều phối vs Vũ điệu vs Hợp tác
- Giải thích các loại hoạt động trong BPMN
- Các loại quy trình phụ trong BPMN
- Cách phân chia và quản lý một sơ đồ BPMN lớn?
This post is also available in Deutsch, English, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.













